Aquaponics FAQ:
You can find here frequently asked questions about Aquaponics or Aquaponics FAQ.
-
What is the process of Aquaponics or how does aquaponics system work?
Aquaponics is an integrated system of aquaculture and hydroponics working together in harmony with each other. The process involves the utilization of fish waste as a source of nutrients for the plants and plants use up the nutrients and filter the waste naturally providing fresh water to the fish. Nitrifying bacteria present in the medium help in converting wastewater into organic manure.
-
What are the advantages of Aquaponics or what are the primary benefits of Aquaponics?
The major advantages of Aquaponics are:
- Low water and power usage
- Environmental friendly
- Basic inputs to the system are fish feed and water
- No use of chemical fertilizers and less use of pesticides
- Easy and fast to grow plants
- Less occurrence of diseases
- Crop produce is available all year round
- Higher production
- A variety of crops and fish can be grown in one system
- Revenue is higher because of the fish and crop produce simultaneously
- Uses less land
-
Why is Aquaponics so important or why do we use Aquaponics?
Aquaponics has become increasingly important because of the un-ending benefits it offers to the urban population. The major factor that makes it important is 90% less water consumption when compared to traditional farming. The system encourages the growth of the plants throughout the entire year with minimal use of chemicals solving the food security and safety possible for the present population. This system also helps people in drought struck areas to produce food which is an interesting and attractive feature.
-
What is the difference between Aquaponics and Hydroponics?
Hydroponics is growing crops in a nutrient medium in the absence of soil and in the presence of inert medium like gravel, sand, etc. Hydroponics is a part of the Aquaponic system. In an Aquaponic system, fish are farmed in coordination with crops, i.e. aquaculture with hydroponics. Aquaponics is more beneficial than hydroponics because the produce is obtained both from crops and fish. Aquaponics uses much less water than normal hydroponic systems.
-
How can one start Aquaponics?
If one is planning to start a small aquaponics farm, then these simple steps can be useful for a quick set up:
- Grow beds are installed with grow media
- The fish tank is set up and water is filled into it
- Add plants to the grow bed
- Test the pH of the nutrient medium and the water in a fish tank
- The establishment of healthy microbes and bacteria is done on the system
- Keep a regular check on the ammonia nitrate levels in the medium
- Make a proper choice of the fish and add them to the tank
-
What can be grown in Aquaponics?
Aquaponics systems are best suited for warm freshwater fish and leafy crops. However, the fish that can be farmed in these systems are tilapia, carps, barramundi, catfish, koi, etc. Ornamental fish like angelfish, guppies, tetras, swordfish, and mollies can also be raised here.
Plants that are grown in aquaponic systems could possibly be lettuce, kale, Swiss chard, watercress, chives, tomatoes, peppers, cucumbers, peas, squash, beans, cauliflower, cabbage, radish, onions, carrots, microgreens, etc.
-
Does Aquaponics save water?
In traditional agricultural practices, the water supplied to the plants is lost either through evaporation or due to run-off and doesn’t reach the plant’s roots properly. Using the best drip irrigation method also cuts the water requirement only by one-fourth and is in no way comparable to Aquaponic systems. The Aquaponic system uses every bit of water over and over again because the run-off water that is not used by the plants is recaptured, sent into the aquaculture tank where it gets nutrient-rich by the fish waste and is possibly returned to the plants after detoxification. So obviously the answer is YES, Aquaponics saves water to a large extent and the only form of water loss in these systems could be leaking or evapotranspiration.
-
Is Aquaponics sustainable?
Sustainability refers to the fact that the technique is potentially useful for the planet, healthy for people, and is economically feasible to undertake. The process of Aquaponics is considered sustainable because of the following reasons:
- Saves water, which is a precious resource
- The need for good soil condition is ruled out
- Farmlands that are barren can also be used to set up an aquaponics farm
- The supply of the nutrient mixture of the crops is natural and consistent
- Produces less waste when compared to other systems
- Reduces the need for long-distance transportation
- Creates financial sustainability due to the produce from the crops and fish.
-
What materials does one need for Aquaponics?
The possible materials needed for building a small aquaponic system are:
- Fish tank made of glass or plastic
- Gravel for the fish tank
- Water pump for circulating water
- Air pump for fish in the tank
- Airstone
- Air tube to connect the air stone and air pump
- Grow bed or medium
- A growing medium like Perlite, coconut coir, clay pebbles, pea gravel, and peat moss, etc.
- pH testing kit
- Fish and plants
- Fish feed
- Some pesticides if required
- Aquarium heater
- Light for the fish tank and grow lights for the crops
-
How do fish waste help plants grow?
The waste from the fish in the water is collected into a tray set up for the hydroponics crops. This wastewater is toxic to the fish but acts as fertilizers to the plant. A naturally occurring bacterium called the nitrifying bacteria converts the wastewater into useful nutrients for the plants to absorb. When plants take up these nutrients, the water is cleaned and sent back to the fish tank.
-
What are the disadvantages of the system?
This integrated system has some disadvantages like:
- The high initial investment for the system setup
- Since it is an integration of two systems, the failure of one may immediately affect the other
- Predicting the ideal conditions for both the systems together is a difficult task
- Not all varieties of crops can be grown in the system
- High electricity usage
- Needs professionally trained hands to work on the system
- Regular monitoring is required
-
What is a growing bed and how deep should Aquaponics grow bed is?
Growing beds in Aquaponics are the containers that are used to grow crops. It is considered that the growing bed can be made of a wide variety of materials, but they should be leakproof, and also it should not allow unwanted chemicals to get into the water such that these alter the pH of water in the grow bed. It is made of materials like plastic, wood, fiberglass, etc. The size of the grow bed should be compatible with the fish tank volume. Generally, the volume of growing bed and fish tank are in the ratio 1:1. For filtering 1000 liters of water, a media volume of 1 cubic meter is needed. For accommodating 1 cubic meter of the media volume, the surface area of the growing bed should be around 1 x 4 m with a depth of 25 cm.
-
What is media Aquaponics?
Hydroponic systems are such that they may or may not use the media for growing plants depending on the choice of plants and the system function. Since Aquaponics is a combination of hydroponics and aquaculture, it is very clear that media-based Aquaponics refers to an internal hydroponic system of growing plants using inert media to anchor the roots of the plants instead of letting the roots float freely in the water.
-
What is a media bed in Aquaponics and what are its dimensions?
The media bed in the aquaponic system is the foundation used in the plant growing area for root development. The materials used for media are expanded clay, peat moss, Perlite, gravel, sand, etc. The media bed is generally an inert medium approximately 6 to 12 inches deep such that this does not affect the composition of water in the tank.
-
What plants do freshwater fish eat?
Freshwater fish feed on algae, moss balls, java moss or riccia, cambomba, egeria, ambulia, myriophyllum, rotala, hydrophila, duck weed, azolla, salvinia, nymphaea, aponogeton, etc.
-
What nutrients are in fish waste?
The fish waste can be categorized into three forms such as urine, solid waste, and ammonia expelled from the gills. Solid waste is from the fish poop and uneaten food which is classified as organic and the remaining two i.e. urine and ammonia are inorganic. The fish waste consists of all the essential nutrients from the food that it was fed.
-
Is Aquaponics better than hydroponics?
Though the two systems share the same techniques for growing plants using nutrient-rich water, there are a few extra improvements Aquaponics can offer when compared to hydroponics such as:
- No or low investment into chemical nutrients
- The nutrient solution is never replaced rather it is topped up due to evaporation
- Considered to offer better productivity
- The need to supervise the system and check for pH levels is done once a week or month
- Aquaponics is a natural ecosystem and can be considered completely organic
-
What nutrients are needed for Aquaponics?
Basically, there are 16 elements required by the plants in an aquaponic system. The three non-mineral-based nutrients required are hydrogen, oxygen, and carbon, which are available from air and water. The remaining nutrients required for the growth of plants are nitrogen, phosphorous, potassium, calcium, magnesium, sulfur, boron, copper, iron, chloride, manganese, molybdenum, zinc, etc.
-
How do plants clean water or do plants filter water?
The water that comes into the plant growing media is free of ammonia toxins and contains nutrients in the form of dissolved fish waste. The plants use up these nutrients from the water for growth and root development, thereby cleaning it up or filtering it from all the dissolved compounds or elements. Also, the plants aerate the water while absorbing nutrients.
-
What is the difference between visible light and grow light during farming?
Visible light or sunlight is a combination of different colours in a spectrum with different frequencies and wavelengths, but grow lights are colour specific and use only two major colour like the blue and red, which are extremely essential for plant growth.
-
What are the best materials for media in the aquaponic system?
It is important to understand that not all hydroponic media are suited in Aquaponics, so the choice should be exclusive and the best grow media suggested for Aquaponics are:
- Clay pebbles
- Expanded shale
- Grow stones
- Lava rock
- Gravel
-
What is the fish to plant ratio in Aquaponics?
Generally, the fish to plant ratio defines the feeding rate ratio of the fish so as to supply enough nutrients to the plants in the hydroponic system. It is estimated that to develop a hydroponic area of 16.7 m², the fish should be fed with 1000 g of feed each day so that the feeding rate ratio is 60 g/m²/day. The feeding rate ratio depends on multiple factors like the hydroponics system, plants being cultivated, chemical composition of water, solid waste loss of filtration, etc.
-
What is the cost of setting up an Aquaponics system?
The minimum average cost of setting up an aquaponics farm in India ranges between 5 and 15 lakh rupees. This is a little higher than traditional farming methods due to the need for equipment for filtration and internal environmental control systems.
-
What are the important properties of a grow media in Aquaponics?
While choosing a grow media for an aquaponic system, the following considerations have to be made:
- It should be inert i.e. the pH of the material should be neutral.
- The size of the media should be appropriate such that it colonizes the bacteria perfectly.
- The weight of the media should be light to medium, not too heavy or too light.
- The depth of the growing media should be approximately around 12 inches.
- The media should not be sharp such that it damages the roots or cuts the hand of the user rather it should be smooth and highly porous in nature.
- The media should not break down and should not be harmful to the system.
- Any media based on limestone should be strictly avoided.
- The media should be cleaned before installing it.
- Introducing the media and adjusting the media is highly important. A close monitor on the pH levels should be done in the beginning, so as to understand the effect of media on the pH of the solution.
- Avoid using coco coir as media.
-
What are the major components of an aquaponic system and why are they important?
There are three major components of an aquaponic system and they are plants, fish, and bacteria. They are considered important because it is due to these components that the entire system functions. The fish grow and live because the bacteria present in the media removes the toxins from the wastewater and supplies it to the plants, which in turn absorb the required nutrients and filter the water to be re-used by the fish in the tank.
-
How do you control the water temperature in the Aquaponics system?
In places with cool temperatures, water or tank heaters are used to control the water temperature in the fish tank. The size of the system defines the no. of heaters required. In warmer areas the tank or system should be planned in a shady place, the lid of the tank should be kept open and aerated. Cooling the water in warm locations needs extra electricity and is difficult. The choice of fish should be proper in such places.
-
Is Aquaponics organic?
Organic produce has some standards designed depending on the country of deployment of the system. The products used in such systems should be majorly organic in nature, but sometimes chemical substances are used to adjust the pH of the water and maintain fish feed in Aquaponics. So, considering these aspects it is clearly known that the fertilizer or nutrients to the plants are supplied from a source that was not organic in nature. Therefore, it is not organic but does not depend on the use of pesticides and insecticides.
-
What are the daily operations of an aquaponic system?
To ensure a healthy system, there are some periodic tasks to be undertaken each day such as;
- Feeding the fish
- Plant seeding, rotation, and harvesting
- Observing and monitoring the farm
- Fish harvesting
- Testing the water quality
- Cleaning the filters and other system equipment
- Operating the system properly
-
Why do aquaponic systems have multiple fish tanks and what is staggered stocking?
For easy management and high production, fish are raised in multiple tanks and stocked sequentially within the aquaponic system and this process is called staggered stocking. This can be further explained as such; when one starts to stock around 50 g of fingerlings, after 6 weeks a second tank is stocked with another 50 g of fingerlings and so on for certain weeks in different tanks. At the end of 24-26 weeks, the first tank of fish would be ready to harvest and similarly in the subsequent weeks the rest of the tanks. This means that every week there could be a harvest when fish are stocked in a staggered fashion.
-
How can one acclimate new fish into the system?
This is a very important step during fish farming and has to be done very carefully. Bringing fish from some other place and stocking them in your aquaponic system may require acclimation so as to make the fish less stressful and improve the levels of bio-security. The acclimation process aims at ensuring the health of the fish and making them disease-free. The fish are quarantined for some time to monitor their behavior and make them get acquainted with the new system.
-
How can one control pests in aquaponic systems?
It is considered that aquaponic systems do not use chemicals for pest and disease control due to the sensitivity of the system. So the basic idea of pest or disease control in Aquaponics refers to the prevention of these things. Some general management techniques that can keep the aquaponic farm healthy are bio-security measures, periodic monitoring and scouting, installing insect screens inside the farm, keeping the farm clean and tidy by removing all the dead and dry matter, etc. If by any chance pests of the disease occur within the system, then identify the proper cause and the type of pest or disease and apply suitable biological control. Allowing beneficial insects can be a possible biological control.
-
What are the common problems within an aquaponic system?
The most common problems with Aquaponics are:
- Ignoring harmful bugs
- Not controlling the temperature of water within the tank
- Stocking too many fish in the tank
- Not testing ammonia levels in water regularly
- Restricted access to fish tanks
-
What should be done if the ammonia or nitrites or nitrate levels are high within the aquaponic system?
When the levels of ammonia or nitrites are high, then the fish should not be fed, remove the uneaten feed from the tank, pump the tank with water for some days and lastly one could salt the system or tank to keep the system balanced.
-
How many fish can be grown in an aquaponic system?
This purely depends on the individual and his investment plans into the system, but by a rule of thumb, it is considered that 5-10 gallons of water can accommodate 1 pound of the fish i.e. 1 or 2 fish approximately. It is advisable not to stock more than 1 pound of fish for three gallons of water otherwise this could create congestion in the system and intoxicate the fish.
-
To whom can the produce from an aquaponic farm be sold?
In India, there is an increasing demand for quality produce and off- seasonal varieties. So, if one is trying to start an aquaponic farm with un-seasonal crops or a non-native variety of fruits and vegetables, then they can market their produce to restaurants and hotels or individual consumers, who are in want of these items.
-
Is there the need to change the water of the aquaponic system?
When water is lost through evaporation and the levels go too low, the water in the tank should be replenished with caution. Water in heavy amounts should never be added to the system otherwise there could be a possible risk of chemical imbalance. It should be added in small quantities as and when loss due to evaporation occurs.
-
What should be done if the plants in the aquaponic system turn yellow?
Plants in the system turn yellow because of iron deficiency, so pure iron chelate should be added to water in the required quantity to help the plants produce more chlorophyll.
-
What factors depend on the size of the fish tank in aquaponic systems?
The size of the fish tank is important for two main reasons. They are:
- Decides the stocking density of the fish.
- Also decides the total volume of grow bed it can supply with water.
-
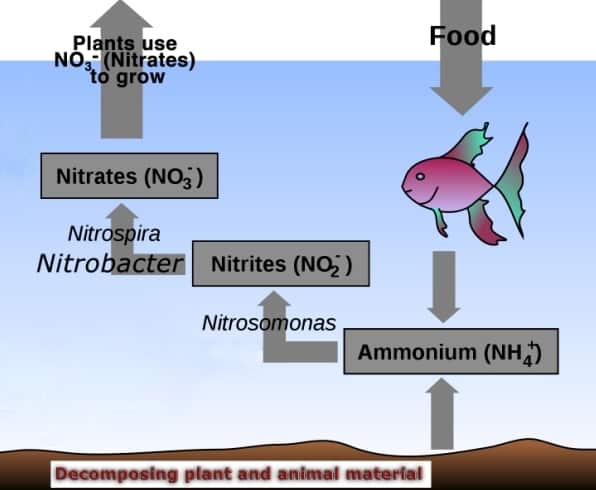
What is the nitrogen cycle in Aquaponics?
The conversion of ammonia and nitrites into less harmful nitrate is called a nitrogen cycle. The Nitrosomonas sp. Bacterium eats ammonia that is generated from uneaten food or decomposed food and converts it into nitrite, which is less poisonous to the fish, but can stop the fish from getting oxygen. So, these nitrites are again processed into nitrates by Nitrobacter sp. The entire process is called nitrification or the nitrogen cycle.
-
Do the aquaponic systems need denitrification set up?
Denitrifying bacteria are anaerobic in nature and do not need oxygen for processing nitrate to nitrogen gas. The process of completely removing nitrogen from the system is called denitrification and is generally required for systems that farm more fish than plants.
In case if you are interested in this: Quail Farming Business Plan.
- How to Make Houseplants Bushy: Effective Tips and Ideas
- Innovative Strategies for Boosting Coconut Pollination and Yield
- Pollination Strategies for Maximum Pumpkin Yield
- The Complete Guide to Chicken Fattening: Strategies for Maximum Growth
- Natural Solutions for Tulip Problems: 100% Effective Remedies for Leaf and Bulb-Related Issues
- Revolutionizing Citrus Preservation: Towards a Healthier, Greener Future
- Natural Solutions for Peony Leaf and Flower Problems: 100% Effective Remedies
- Maximizing Profits with Avocado Contract Farming in India: A Comprehensive Guide
- Natural Solutions for Hydrangea Problems: 100% Effective Remedies for Leaf and Flowers
- The Ultimate Guide to Choosing the Perfect Foliage Friend: Bringing Life Indoors
- From Sunlight to Sustainability: 15 Ways to Use Solar Technology in Agriculture
- The Ultimate Guide to Dong Tao Chicken: Exploring from History to Raising
- The Eco-Friendly Makeover: How to Convert Your Unused Swimming Pool into a Fish Pond
- Mastering the Art of Delaware Chicken Farming: Essentials for Healthy Backyard Flocks
- 20 Best Homemade Fertilizers for Money Plant: DIY Recipes and Application Methods
- How to Craft a Comprehensive Free-Range Chicken Farming Business Plan
- Brighten Your Flock: Raising Easter Egger Chickens for Beauty and Bounty
- How to Optimize Your Poultry Egg Farm Business Plan with These Strategies
- Subsidy for Spirulina Cultivation: How Indian Government Schemes Encouraging Spirulina Farmers
- Ultimate Guide to Raising Dominique Chickens: Breeding, Feeding, Egg-Production, and Care
- Mastering the Art of Raising Jersey Giant Chickens: Care, Feeding, and More
- Ultimate Guide to Raising Legbar Chickens: Breeding, Farming Practices, Diet, Egg-Production
- How to Raise Welsummer Chickens: A Comprehensive Guide for Beginners
- How to Protect Indoor Plants in Winter: A Comprehensive Guide
- Ultimate Guide to Grow Bag Gardening: Tips, Tricks, and Planting Ideas for Urban Gardeners
- Guide to Lotus Cultivation: How to Propagate, Plant, Grow, Care, Cost, and Profit
- Agriculture Drone Subsidy Scheme: Government Kisan Subsidy, License, and How to Apply Online
I will start my aquaponic farming in a near future.
Thanks for the information