Black Gram Cultivation (Urad Dal) Information:
Today, we discuss the topic of black gram cultivation practices or urad dal cultivation methods.

Introduction:
Black gram (Vigna Mungo L.) is popularly known as “Urad”, is one of the most important pulses crop, grown across India. The Urad crop is resistant to adverse climatic conditions and improves soil fertility by fixing atmospheric nitrogen in the soil.
This crop is grown primarily for its protein-rich seeds and used as daal and as the main ingredient in breakfast snacks like dosa, idli, vada & papad.
Local Names for Black Gram (Urad Dal) in India:
Urad Dal (Hindi), Minumulu (Telugu),Ulundu Paruppu (Tamil), Uzhunnu Parippu (Malayalam), Uddina bele (Kannada), Masakalai dala (Bengali), Biri dali (Oriya), Kaali Dal(Marathi), Adad Dal (Gujarati).
Commercial Varities of Black Gram in India:
LBG-20,T-9, Uttara, LBG-623, KU-91-2, Vamban-2, Azad Urid-2, KU-3-1, WBG-26, WBU-108 , TU-94-2,ADT-5, Azad-1, Azad-3, M-391,DU-1, IPU 2-43, Mash-114, Mash-479, WBU-109,PU-31, PU-40, Sekhar-1, Sekhar-2, Sekhar-3, LBG-7658, LBG-752.
Crop Calendar in Black Gram Cultivation:
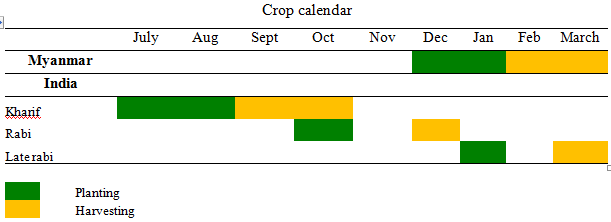
Agro-Climate required in Black Gram Cultivation:
This crop prefers dry weather condition with an ideal temperature range between 25 C to 35 C. Maturity crop period should coincide with the dry weather the condition for high yield and good quality seeds, this is one of the main criteria to decide the time of planting.
Soil requirement in Black Gram Cultivation:
Soil in Black Gram cultivation should have a neutral pH. Loam or clay loam soils are best-suited soils for its cultivation. Adding higher organic matter in the soil will result in vigorous seed production.
Selection of land and it’s Preparation in Black Gram Cultivation:
The field selected for seed production must not have been sown with a black gram in the previous years. This is done to avoid volunteer plants that cause admixture. Fields continuously cultivated with black gram may harbor root rot or wilt pathogen.
Seed selection in Black Gram Cultivation:
Seeds used in sowing must be from an authorized source. Seeds must be genetically pure and having fine quality. Seeds used for sowing in Black Gram cultivation must also be vigorous so that we can obtain a good field stand. Seeds must be thoroughly checked for diseased seeds, hard seeds, shrunken, deformed seeds, and immature seeds.
Seed rate and Treatment in Black Gram Cultivation:
Seed rate depends on the variety the seed selected. Usually, an average of 8 to 10 kg per acre is sufficient.
Black gram seeds should be treated with seed treating fungicide to reduce infection by fungal pathogens from the soil. Black gram seeds are treated with Bavistin 2 grams for every kg of seeds. Organic fungicide like Trichoderma viridi is also available for pulses @ 4 grams/kg.
Sowing and Spacing in Black Gram Seed Cultivation:
The Black Gram seeds are sown @ 2 cm depth with a spacing of 10 cm and 30 cm between rows in the main field. Irrigation management in Black Gram Cultivation:- Irrigation/Water management in Black Gram Cultivation:- Black gram crop is very sensitive to irrigation. Fields must be constantly monitored for any drought conditions. If this crop is not irrigated properly, pulse crop shed flowers. Plants without water produce seeds that are small and hard with low vigor. Because of this problem Black Gram crop must have sufficient water supply.
The field should be irrigated immediately after sowing followed by lite irrigation on the 3rd day. Then, irrigation should be carried out based on the need (Usually when the field becomes dry). Water supply during the flowering of the crop, pod formation & seed development must be provided for quality
output.
Fertilizers in Black Gram cultivation:
Basal fertilizers application alone may not be sufficient for the seed crop. It is mandatory to provide nutrition during the heavy growth of crop and seed formation period. The nutrient needed by the rapidly developing pulse seeds is provided through foliar feeding.
Nutrient solution preparation is done by soaking the following chemicals in water (100 lit). This solution is sprayed 25 to 35 days after seed sowing followed by another spray in 40 to 50 days. Below table lists the items for preparing the nutrient solution.
| Chemicals / Fertilizers | Quantity to be soaked in 100 Litre |
|
1. Urea |
4.0 |
|
2. D.A.P. |
1.0 |
|
3. Muriate of Potash |
0.6 |
|
4. Potassium sulfate |
0.02 |
|
5. Succinic acid |
0.02 |
|
6. Teepol |
0.04 ml |
Weed control in Black Gram cultivation:
Immediately after sowing and watering, Basalin weedicide is sprayed by dissolving 2 ml of Basalin/liter water. The weedicide spraying must be done within 3 days of sowing. If it is done later, it can damage the crop. Applying weedicide will control the early growth weeds, to control later emerging weeds in the crop, manual weeding should be done after 2 weeks.
Pests and Diseases in Black Gram cultivation:
The main pest in the Black Gram crop is stem fly. This pest affects the crop at the early stages by causing drying and withering plants. During the growth phase, major pests like leaf hopper, aphid, white fly affect the field crop. These pests
should be controlled by spraying either dimethoate, phosphomidan or mehyldematan, @ 2 ml/litre.
During the growing phases of the seed crop incidence of yellow mosaic can be observed. The affected crop shows yellow mottled symptoms. These plants can be rouged out as and when they are seen. Whitefly is the culprit in spreading this disease, removal of the affected plants is followed by an insecticide spray as mentioned above. Apart from this, black gram crop is also affected by root rot, wilt and these are to be removed and the affected area of the field should be sprayed using 0.1% Bavistin solution. Rarely the Black Gram crop is affected by Powdery mildew and it is noticed by the presence of white powder deposits on the leaves. Leaf spot of Cercospora can be noticed by the presence of brown spots. The Powdery mildew and cercospora can be controlled by spraying 1% Bavistin solution.
Harvesting of black gram crop:
The ripened pods can be collected from the plants in one or two pickings and dried on the floor. In case, If the plants come to harvest, then the crop should cut and the plants spread over the floor to dry. The plants become dry and turn into black and pods may start splitting. The plants should be beaten using pliable sticks to prevent damage to seeds. Then seeds are separated from pods. These plants after harvesting can be used as fodder for animals.

The yield of Black Gram:
Basically, Yield depends on the variety of seed selected and field management, with hybrid varieties it is possible to achieve yield from 800 kg -1100 kg /acre.
Read: How to Prepare Garden Seedbed.
Please give detailed information on Ajwain farming, Lentil farming, Dill seed farming and Sorghum sudan grass farming.
Good information for better yeilding.
Very comprehensive explanation. Good luck. Ravi
Thank you for the valuable information. Where do we get the quality reliable SEEDS for planting. Please share the address and other details. How much will be the market price per quintal and how to market.
Thank you and appreciate your help in finding the good resource for SEEDS.
Ram