Dairy Housing Systems
Dairy Housing is required to protect the animals from inclement weather conditions, provide a clean, comfortable stay for good animal health and efficient management. Inadequate and improper housing planning results in additional labor charges and increased costs in the maintenance of sheds. Adequate housing to dairy animals is aimed at increased milk production, better labor utilization, better animal health, disease control, better care, and management of animals resulting in the production of high-quality milk resulting in a remunerative price and better profit of the dairy farm. In this article we also discuss the below topics about Dairy housing systems;
- The different housing systems of dairy animals
- What are the roles of housing in dairy animals
- What are the essential requirements of dairy housing
- How much land is required for a dairy farm
- The housing of dairy animals
Proper dairy housing based on scientific principles is an important aspect of dairy animal management for obtaining maximum productivity of the animals. A clean and comfortable shelter increases the comfort level of dairy animals and results in their good health. The necessary criteria for housing dairy animals are animal health and comfort, hygiene, protection from predators, diseases, efficient and economical use of labor, and provision of a suitable environment for hygienic milk production. In this dairy housing system, shelter is provided along one side of an open paddock under which animals can retire when it is very hot or cold or during rains.
Proper dairy housing based on scientific principles is an important aspect of dairy animal management for obtaining maximum productivity of the animals. A comfortable and clean shelter increases the comfort level of the animals and results in their good health.
Efficient management of dairy animals will be incomplete without a well-planned and adequate housing of dairy animals. Improper planning in the arrangement of animal housing can result in additional labor charges and that curtail the profit of the owner. During the erection of a house for dairy cattle, care must be taken to provide comfortable accommodation for individual cattle. No less important is the proper sanitation, durability, and arrangements for clean milk production under convenient and economic conditions, etc.
A Step-by-Step Guide to Dairy Housing Systems – Types, Design, Layout, and Requirements

Key Aspects of Dairy Housing
Six important aspects of dairy housing are as follows;
- Space – Availability of sufficient space allows the animals to move freely and gives them easy access to feed and water.
- Feed – Arrangements are made in dairy housing so that animals can eat well-formulated feed. The animal feed is available daily for at least 21 hours.
- Water – Accessibility of clean water for at least 21 hours daily for dairy animals.
- Air – Dairy housing access to fresh and clean air.
- Light – Availability of sufficient natural light and provision to maintain 6 hours of darkness for farm animals is essential for optimum production.
Good Ventilation for Dairy Housing Systems
A proper dairy housing climate is one of the pre-conditions for maintaining an excellent environment within the various housing systems. Then, it has a great effect on the well-being and health status of animals, and overall performance. Conditions must be created to enhance the animal’s inherent ability to control its temperature. So, ventilation is essential for the supply of fresh air, with the emphasis on maintaining a suitable air quality under any weather condition over a long period. Also, adequate ventilation is required for the removal of harmful gases, avoidance of moisture accumulation, and the removal of heat produced by dairy animals.
A more specialized dairy housing system combines different management-related aspects at a dairy farm such as milking, feeding, health care, and manure management. The housing of dairy animals needs quite a high investment, but will also open possibilities to get high returns. Key issues for high returns are; reduction of losses, efficient feeding, and efficient utilization of manure, etc. Also, there are advantages of individual cow management like heat detection, health control, and treatments, etc.
The main guidelines for proper dairy housing design are:
- Constructing building facilities to increase comfort and manageability of dairy animals;
- Improving labor efficiency by providing desirable working conditions;
- Planning with the emphasis on logistical lines for cow traffic patterns;
- Maintaining adequate ventilation in enclosed barns under all-weather circumstances;
- Planning an appropriate manure handling and storage system, which complies with legal requirements for environmental control;
- Providing sufficient space per cow at the feeding rack;
- Keeping apart maternity and separation pens to provide hygienic circumstances;
- Having sufficient natural or artificial lighting available;
- Providing sufficient drinking space for all animals;
- Keeping holding area separate from free stall area.
Selection and Location of Dairy Housing Systems
Proper dairy housing is conducive to good health, comfort, and protection from inclement weather and feed for optimal production. For the construction of dairy farm buildings selection of the site is most important.
Factors to be considered when choosing land for dairy housing are fertile soils, no evidence of flooding during the wet season, convenience for transportation, proximity to milk collection centers, and access to supplies for farming and, year-round supplies of sufficient clean water. Distance from factories and to urban areas should also be key influences on location.
All dairy animals require shelter for protection and comfort. Then, they can perform better under favorable environmental conditions. Animal housing needs initial capital to the extent the dairy farmers can afford it. The animals are to be protected from high and low-temperature levels, strong sunlight, heavy rainfall, high humidity, snowfall, and strong winds. The comfortable temperature level for dairy breeds of cattle, buffaloes, and goats is 15C to 27C. Climatic stress occurs when the temperature level goes 50C below or above this range.
High humidity combined with high-temperature levels causes more stress to animals in the tropics. Strong winds further aggravate the conditions in the tropics and temperate climate conditions. Several methods are available to provide relief from hot weather conditions for lactating dairy cows. In tropical and sub-tropical climates, the well-ventilated shed is a necessity at points of high heat stress like feed barns, loafing areas, and holding areas. It is very important to provide a sufficient flow of air through the building in which the animals are kept to ensure optimum thermal conditions for dairy animals.
Availability of land
There should be vast areas to construct dairy housing and give way to the future expansion of the dairy farm.
- At least 2-3 acre land is required for 200 cow’s accommodation.
- For 2 cows 1-acre land is necessary for fodder production.
Drainage system
Proper drainage of rain and subsoil water must be provided to keep a healthy environment and to protect the building from dampness.
Floor
Floors must provide a comfortable footing, be firm and durable, and should direct excess liquids towards competent drainage, to provide a dry walking surface
- Floors should provide sufficient traction.
- Floors should be clean and dry.
- Floors must be smooth and in a good condition.
- Rubber will improve walking
Checking the floor is mainly important for two major problems on dairy farms lameness and estrus detection. The quality of the floor of the barn is of major influence on the incidence of lameness, which is a problem on most dairy farms. An incidence of about 25% (cow cases per year) is considered “normal” but costs too much money.
The floor is smooth, clean, and dry
A clean and smooth floor is a prerequisite for a proper grip that allows cows to walk comfortably, without restrictions. If the floor is not smooth, injuries due to local pressure on the sole of the claw can occur, resulting in injury and lameness. Also, if there is a layer of manure present, the claws will remain wet and soft. The effect of a slight slope compared with a flat surface and they concluded that a slope maintains a drier environment for the feet, an important property that appeared to prevent the formation of the hind-claw lesion, even as animals stood on the surface for up to 4.5 hours per day. Floors in walking areas must be kept as dry and clean as possible.
Availability of water
Plenty of water is required for farm operations like washing, fodder cultivation, processing of milk and byproducts, and drinking.
Electricity
- It should be available at the site.
- It is needed for operating various machines used in the dairy farm and is the light source to the animals.
Disease control
- The dairy animal house should be designed properly to affect disease control.
- Easily drained floor, washable walls will control the spread of some dairy animal diseases.
- Designing a suitable drainage system for the hygienic disposal of wastes is required for preventing disease.
- Also, a dampness-resistant surface will reduce the high humidity, which is the predisposing cause of respiratory disease in young dairy animals.
Advantages of Proper Dairy Housing Systems
In case if you miss this: Livestock Farming Tips, Ideas, Techeniques and Secrets.
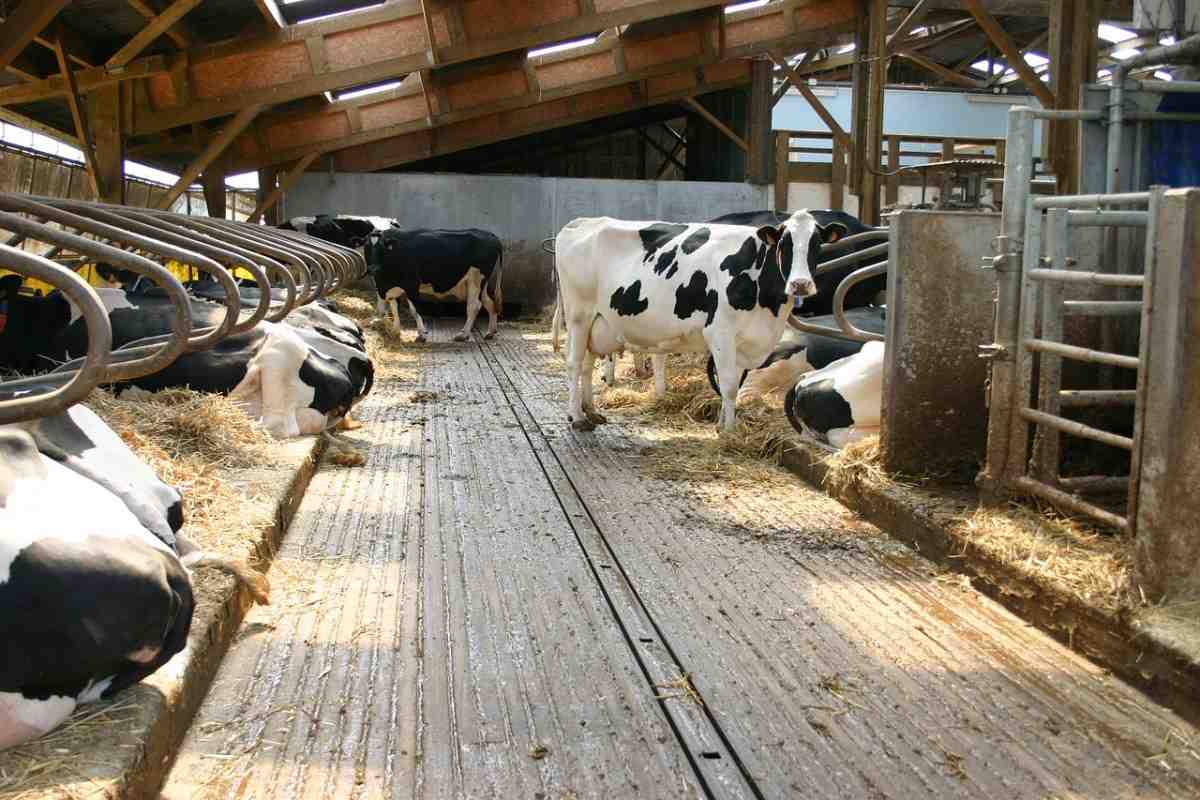

- Proper housing is to protect animals from sunburns, rain, hot and cold winds of inclement weather conditions.
- To provide clean and comfortable shelter for dairy animals.
- Providing better accommodation at a cheaper cost.
- To protect animals from wild animals.
- Maintain optimum weight by setting feed levels based on a reliable, quality supply of feed. Any changes in animal eating habits are quickly spotted and rectified. Also, help to save costs on feed wastage.
- Increased production of milk.
- Better utilization of labor.
- Production of higher quality milk.
- Better health of animals.
- Decrease in the mortality rate of claves.
- Proper disease control.
- Better care and supervision of animals.
- Better productive and reproductive efficiency of animals.
- Proper and controlled feeding of animals.
- Increasing pride of dairy farmers.
- Encouragement to other dairy farmers.
Important Points in Dairy Housing Design
What is important in designing housing for dairy animals?
Some important aspects taken into account in designing housing for dairy animals are;
You should think about;
- Comfort
- Safety
- Economy
- Convenience.
This involves protection from rain and extremes of heat and cold and strong wind and adequate ventilation.
The following points must be considered before planning and designing animal houses;
- It should be of attractive appearance
- It should minimize labor cost
- The efficiency of the operation should be increased
- It should have resale value
Dairy Housing Layout
The housing layout of dairy animals is the most important document in the design process. This is where all the free-stall barn components come together to develop a plan that is functional, flexible, and cost-effective.
Some Important factors of Economic Importance in Planning a Good Layout of Dairy Farm Housing;
- Topography of the land
- Capital availability
- Stock density and feeding policy
- Effective supervision of farm operation
- Use of labor-saving devices
- Fodder conservation
- Other resources of fodder
- Type of farm buildings
The dairy house facilitates various farm activities such as milking, feeding, and cleaning efficiently. Also, the animal house provides comfort to the animals for optimal milk production and protection against unfavorable weather conditions, for example, heat, rain, and wind.
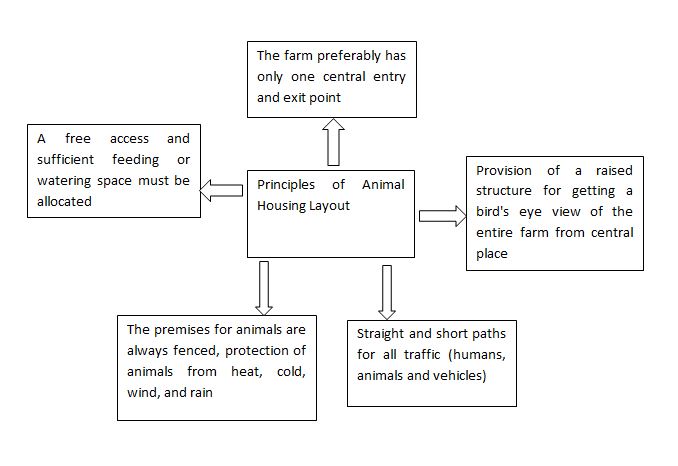
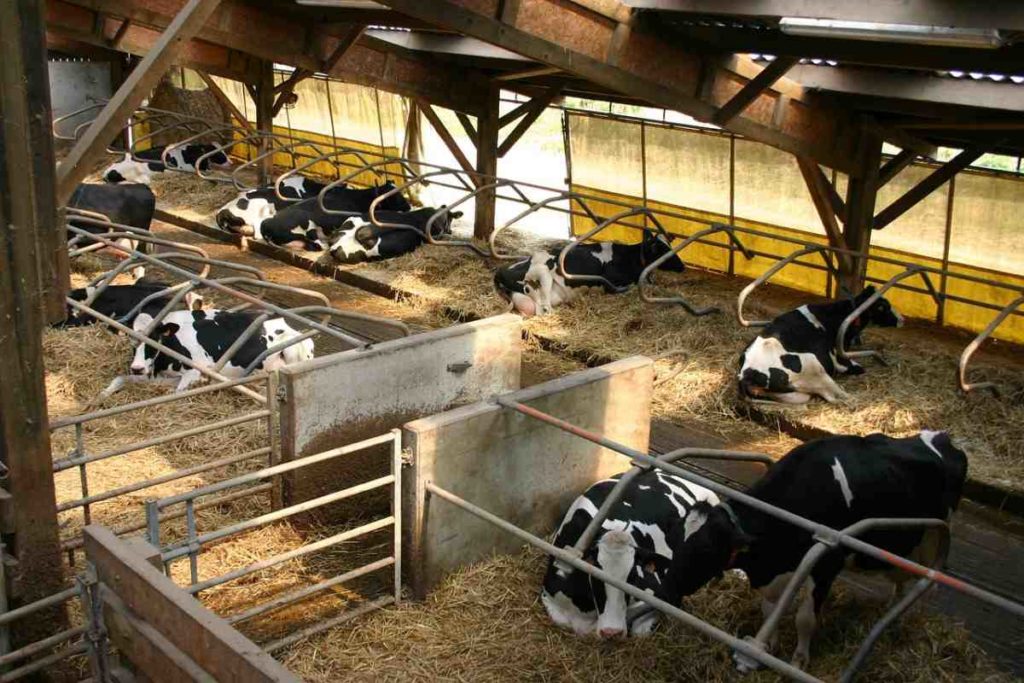
Different Types of Dairy Housing Systems
Traditional animal shelters have grown out of the needs, resources, and ingenuity of dairy farmers. Building design and construction materials mainly affect the thermal comfort inside dairy shelters. Efficiently designed sheds can help less the thermal stress thereby increasing feed intake, milk production, and reproductive efficiency. It is easy to understand that unless cattle are provided with good housing facilities, the animals will move too far in or out of the standing space, defecating all around and even causing wasting of feed by stepping into the mangers. The dairy animals will be exposed to extreme weather conditions all leading to bad health and lower production.
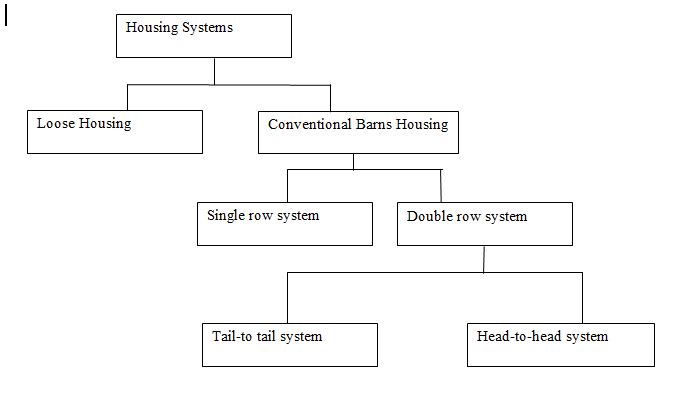
Under different climatic, geographical, and economic conditions prevailing in India, designing an ideal set of building for dairy animals throughout the country is impossible. Usually, there are two systems of housing for dairy animals;
- Loose housing and
- Conventional barns
Flow Chart Diagram for Types of Dairy Housing Systems
Loose Housing for Dairy Animals
Loose housing for dairy animals is a system of housing in which animals are kept loose in an open paddock throughout the day and night except at the time of milking and treatment. Common feed manger and water tank are provided and concentrates are fed at the milking time which is done in a separate milking barn in which cows are secured at milking time and are milked. Then, the open paddock is enclosed using half walls or plain wire fences of convenient height. Some features of loose dairy housing system are as follows;
- Construction cost is significantly lower than the conventional type.
- Facilitate easy detection of animals in heat.
- Animals feel free and prove more profitable with even minimum grazing
- Animals get optimum excise which is important for better health production.
- Overall better management can be rendered.
This housing system comprises of keeping animals loose in an open paddock or pasture throughout the day and night except at milking time. A common watering tank and common fodder manger is provided within the shed and concentrates are fed at the time of milking in a separate milking barn.
Advantages of Loose Housing Systems;
- The loose dairy houses are cheaper to construct, easier to expand, and flexible in utility.
- Animals are more comfortable in a loose housing system as they move about freely.
- Detection of heat in animals is easier.
- Animals get sufficient exercise which is extremely important for better health production.
- The cost of construction is cheaper.
- Future expansion is possible.
- The animal can be kept clean.
- Common feeding and watering arrangement is possible.
- In a loose housing system, clean milk production is possible because the animals are milked in a separate milking barn.
Disadvantages of Loose Housing Systems;
- It is not suitable for temperate Himalayan regions and heavy rainfall regions.
- It requires more floor space.
- There is competition for feed.
- The attention of individual animals is not possible.
- A separate milking barn is required for the milking of animals.
Conventional Barns or Stanchion Barns
In this housing system, the animals are confined together on a platform and secured at the neck by the neck chain. The dairy animals are fed as wells as milk in the same barn. These barns are covered with roofs and the sidewalls are closed with windows or ventilators located at suitable places to get more ventilation and lighting. Also, it is applicable for temperate and heavy rainfall regions. This type of housing can be utilized for the tropical region with slight modification.
Advantages of Conventional Barns Housing System
- The animals are less exposed to the harsh environment.
- The animals can be kept clean.
- Diseases are better controlled.
- Individual care can be given.
- A separate milking barn is not required.
Disadvantages of Conventional Barns Housing System
- The cost of construction is more.
- Future expansion is difficult.
- Conventional Barns are not suitable for hot and humid climatic conditions.
Though, the conventional dairy barns are comparatively costly and are now becoming less popular day by day. By this system dairy animals are more protected from adverse climatic conditions.
The following barns are generally required for proper housing of different classes
Single row system – In a single row system, 12 to 16 numbers of animals can be kept.
Double row system
- If it is greater than 16 numbers, then a double row system is preferable.
- Up to 50 animals can be maintained in a single shed in a double row system.
- The distance between 2 sheds must be greater than 30 feet or it should be twice the height of the building.
The double row system is two types. They are;
- Tail to tail system
- Head to head system
Tail to Tail System
In tail to the tail system, under the average conditions, 125 to 150 man-hours of labor are required per cow per year. Time spent at the back of the cows is about 4 times more than the time spent in front of them. In tail to the tail system, the central passage with a gutter on both sides of the central passage is located in the center of the shed.
Advantages of the tail to tail system
- The lesser danger of diseases spread from animal to animal
- Dairy animals can always get more fresh air from outside
- All animals get fresh air
- Spreading diseases through the respiratory system is minimum
- Cleaning is easy
- A wide middle alley is of great advantage in cleaning and milking of animals.
Head to Head System
The main advantage of head to the head system is that the distribution of feed and fodder to the animals can be done simultaneously on both sides of feed managers. In head to the head system, the animals can be displayed to the visitors in a better manner. The animals can enter the sheds easily.
Advantages of head to head system
- Dairy cows make a better showing for visitors when heads are together
- The animals feel easier to get into their stalls.
- Cow feeding is easier; both rows can be fed without backtracking.
- It is better for narrow barns.
- Getting animals into the shed is easy.
- Feeding animals also easy.
Disadvantages of head to head system
- Milking supervision is difficult.
- Possibilities of transmission of disease are more.
- Not labor-friendly.
Simple Design Features for Dairy Housing Systems
You may also check this: Tilapia Fish Farming In Tanks.
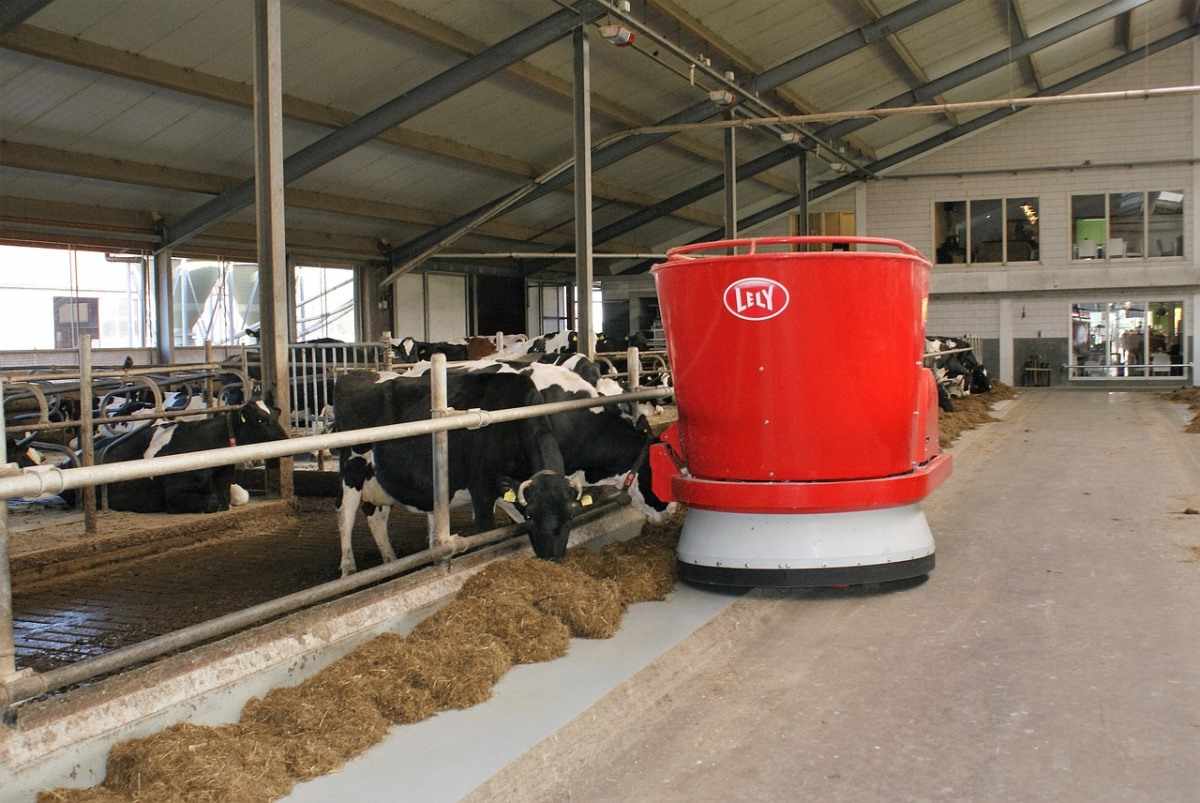

The Main Objectives of Dairy Housing are;
- Efficient management requires well-planned and adequate housing.
- Housing should modify the micro-environment inside them by reducing climatic stress.
- Better care and supervision of animals and optimum utilization of labor and time.
Good dairy housing systems have many simple design features to improve cow and farmer comfort. In hot climates, the below features are very important;
- Sufficient yard space
- A plentiful supply of drinking water
- Cement floors must be sloped for manure management and be non-slip for cows’ comfort.
- There must be sufficient watering points or troughs for all stock.
- Good sanitation is important for dairy housing.
- Sufficient feeding trough space for each cow
- Wire fences useful instead of solid walls to avoid restricting airflow
- Painting buildings white to maximize reflection
- Orientating buildings to maximize winds and shade
- Being very wary of steep slopes.
Design Consideration for Animal Houses
House must be designed to have some points in mind;
- Reduce heat gain – planting trees, reduce ground reflection by coverage of landscape, attached shade
- Promote heat loss from the animal house by radiation and conduction, cooling of exterior surface, minimizing solar projection by suitable materials of the roof, and walls, etc., adequate ceiling height and insulation.
- Reduction in heat liberation inside the building by keeping animals in pens low.
Drinking-Water Provision for dairy housing
- Water at the farm will be used for drinking and washing of animals, washing of floors, utensils, and irrigation.
- Based on the season, the food and physiological status of animal’s requirements may increase.
- Buffaloes need more water than cows. The water trough may be round or rectangular.
- Have a slope to one side ending in a hole to allow easy draining and cleaning.
Housing Plan Preparation for Dairy Animals
Plan preparation is necessary for the construction of animal houses.
Site plan
- It is used to locate the dairy housing where the buildings are to be erected.
- It must contain details of various building arrangements, road formation, and space between buildings, etc. will be located.
Floor plan
- It is the aerial view of the different floor structures to be erected within a farm building.
- It must contain details like dimensions of the building, location of ventilators, and doorways will be marked in the floor plan.
Elevation
The view of the whole farm building will be shown in the elevation.
Cross-section
- It gives details of building foundation, flooring type, walls, and building roof.
- The internal fittings, partition, feeding, and securing devices must be clearly shown.
Orientation
- The farm housing can be constructed facing the road, and other buildings can be turned at an angle to the road or reversed to take advantage of the prevailing wind and sunlight.
Roof
- The roof is provided to protect dairy animals from hot sun and rain. Also, it protects the internal structures.
- It should be of a simple type and cheap materials have to be used for animal buildings.
- One of the necessary qualities required for roof material in tropical conditions is to have high insulation value.
Dairy Housing Sanitation
Dairy housing sanitation is significantly important in terms of dairy cattle health management. The amount of dung and urine produced by animals is variable due to differences in feed and water intake, which in turn is strongly related to body weight and production intensity. A large amount of dung and urine are excreted by dairy cattle due to the types of feed they fed on and their unique digestive system. If it is not timely and properly cleaned the dairy house, manure becomes a source of disease-causing agents to both humans and livestock and a threat to clean milk production. On the other hand, a clean barn is critical to the cattle health, for clean milk production and profitability of the farm. So, the objective of this section is to provide the trainee with a basic skill of hygienic measures of dairy barn and disposal of wastes, and the benefit, management, and utilization of manure.
- Economical Aquaculture: A Guide to Low-Budget Fish Farming
- 15 Common Planting Errors That Can Doom Your Fruit Trees
- How to Make Houseplants Bushy: Effective Tips and Ideas
- Innovative Strategies for Boosting Coconut Pollination and Yield
- Pollination Strategies for Maximum Pumpkin Yield
- The Complete Guide to Chicken Fattening: Strategies for Maximum Growth
- Natural Solutions for Tulip Problems: 100% Effective Remedies for Leaf and Bulb-Related Issues
- Revolutionizing Citrus Preservation: Towards a Healthier, Greener Future
- Natural Solutions for Peony Leaf and Flower Problems: 100% Effective Remedies
- Maximizing Profits with Avocado Contract Farming in India: A Comprehensive Guide
- Natural Solutions for Hydrangea Problems: 100% Effective Remedies for Leaf and Flowers
- The Ultimate Guide to Choosing the Perfect Foliage Friend: Bringing Life Indoors
- From Sunlight to Sustainability: 15 Ways to Use Solar Technology in Agriculture
- The Ultimate Guide to Dong Tao Chicken: Exploring from History to Raising
- The Eco-Friendly Makeover: How to Convert Your Unused Swimming Pool into a Fish Pond
- Mastering the Art of Delaware Chicken Farming: Essentials for Healthy Backyard Flocks
- 20 Best Homemade Fertilizers for Money Plant: DIY Recipes and Application Methods
- How to Craft a Comprehensive Free-Range Chicken Farming Business Plan
- Brighten Your Flock: Raising Easter Egger Chickens for Beauty and Bounty
- How to Optimize Your Poultry Egg Farm Business Plan with These Strategies
- Subsidy for Spirulina Cultivation: How Indian Government Schemes Encouraging Spirulina Farmers
- Ultimate Guide to Raising Dominique Chickens: Breeding, Feeding, Egg-Production, and Care
- Mastering the Art of Raising Jersey Giant Chickens: Care, Feeding, and More
- Ultimate Guide to Raising Legbar Chickens: Breeding, Farming Practices, Diet, Egg-Production
The article for very useful for new start-up dairy farming. Help mecca lot to improve my dairy farming project in Morogoro, Tanzania, East Africa.
An interesting compilation.