Green Gram Cultivation Information Guide:
Today, we learn the topic of Green Gram Cultivation practices or farming methods of a green gram or Moong bean cultivation.
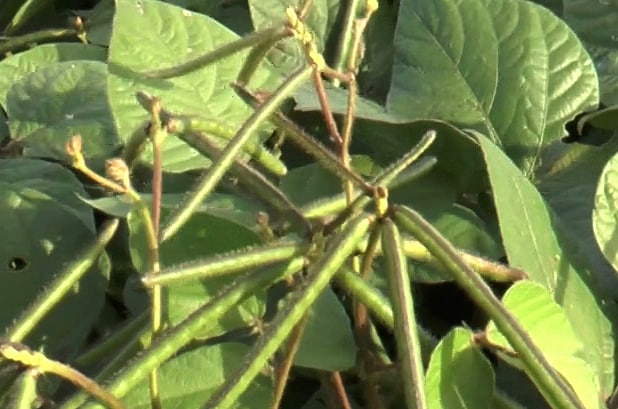

Introduction of Green Gram:
Green gram is popularly known as “Moong Dal “ in India and is basically a tiny circular shaped bean that is green in color. Green gram is one of the main pulse crops in India. It is widely cultivated throughout Asia, including India.
Green gram provides protein requirement for a vegetarian population of the country. It is a protein-rich diet. In India, it is consumed in the form of the whole pulse as well as split pulse. Kitchidi made with moong dal or Green gram is recommended to the aged or ill people as it is easily digestible diet. In the Indian average diet, roti with Moong dal chawal and Moong dal is considered an important ingredient.
Health Benefits of Green Gram:
Some of the health benefits of Moong are listed below.
- Green gram or moong dal is a good source of protein.
- Green gram helps you lose weight.
- Green gram is a good source of fiber and iron.
- Green gram helps control blood pressure.
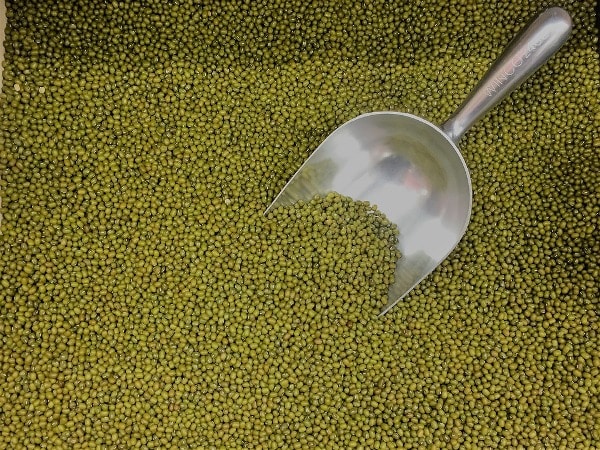

Local Names of Green Gram in India:
Pesallu/Pesara pappu (Telugu), Mung/Moong Dal (Hindi), Hesar Kalu(Kannada), Moog dal (Marathi), Cheru payaru (Malayalam), Paasi paruppu(Tamil), Mug (Gujarati), Mung, and Mmug dal (Bengali).
Hybrid Varieties of Green Gram in India:
Some of the hybrid varieties of green gram are: RUM-1,HUM-12,BM-4, PDM-54, JM-72, K-851, and PDM-11.
Agro-Climatic conditions for Green Gram Cultivation:
Best climatic condition for Green gram cultivation is warm humid and within a temperature range of 25°C – 35°C, with moderate rains of 85 to 100 cm, well distributed throughout its growing period of 100 days.
Read: Successful Poultry Farming Tips.
Best season to grow Green Gram:
Usually, March to June period has high temperature and low humidity and this will keep insects and diseases at their lowest. Green Gram is cultivated during warm and wet Kharif season in North India whereas in South India in the mild winter season.
Soil requirement in Green Gram Cultivation:
Green Gram can be cultivated in a wide range of soils, from black cotton soils in North India red laterite soils in South India and sandy soils in Rajasthan. For best production of Green Gram One should select the soil like well-drained loamy to sandy loam soil. Avoid water logging soils and saline soils as they are not suitable for green gram cultivation.
Field Preparation in Green Gram Cultivation:
The main field selected for Green Gram cultivation must not have been sown with moong or green gram in the previous seasons to avoid volunteer plants that will cause admixture. Prepare the main field by plowing for fine tilth and form channels and beds for Green Gram cultivation. To supplement the soil with proper nutrients, apply lime at the rate of 2 tonnes/ha along with Farm Yard Manure @ 12.5 tonnes/ha or composted coir pith at 13 tonnes/ha to get an extra yield of about 15% to 20%.
Seed Rate in Green Gram Cultivation:
Seed rate depends on the variety of seed and that may vary from 8 to 10 kg/acre.
Seed Selection in Green Gram Cultivation:
Seeds used for cultivation must be from a genuine authorized source which will help you to select proper seed that has genetic purity and seeds must be vigorous to have good field stand. In the process of seed selection, one must check for diseased seeds, hard seeds, shrunken seeds immature seeds, deformed seeds.

Read: Mushroom Training Centers in India.
Seed Treatment in Green Gram Cultivation:
Treat the seeds with Thiram or Carbendazim at 2 grams/kg of seed 1 day before sowing the seeds or Pseudomonas fluorescens @ 10 grams/kg seed or with talc formulation of Trichoderma viride @ 4grams/kg of seed. First, treat the Green Gram seeds with Biocontrol agents and then with Rhizobium.
Fertilizers and Manures in Green Gram Cultivation:
Apply the following fertilizers basally before sowing Green Gram seed.
10 cartloads (5 tones) of well-decomposed compost like cow dung or any other good compost should be spread along with a basal application of 120 kg superphosphate and 20 kg urea/acre.
- Irrigated condition : 50 kg P2O + 25 kg N + 50 kg P2O5 + 20 kg S /ha.
- Rainfed condition : 25 kg P2O5 + 12.5 kg N + 10 kg S /ha.
Read: How to Test for Seed Viability.
Sowing in Green Gram Cultivation:
Dibble the Green Gram seeds making a space of 30 cm x 10 cm in Green Gram farming. In the case of bund crop, dibble the seeds with 30 cm spacing.
Irrigation in Green Gram Cultivation:
Irrigation should be done after sowing, followed by life irrigation on the 3rd day. Irrigate at intervals of 6 to 9 days depending upon climatic conditions and soil type. Irrigation must be provided at flowering & pod formation stages. Make sure soil has proper drainage and avoid water logging at all stages of plant growth. Should apply KCl at 0.5% as a foliar spray during the vegetative stage of the crop, if there is any moisture stress.
Weed control in Green Gram Cultivation:
As soon as sowing and irrigation are done Basalin weedicide should be applied by dissolving 2 ml of Basalin/ liter of water. The spraying of weedicide must be done within 3 days of sowing the seeds. If done later, it can damage the seed crop. To manage and control later emerging weeds in the crop, manual weeding should be preferred 1 month after of sowing.
Pests and Disease control in Green Gram Cultivation:
Stem fly is the main pest found in this crop. This pest affects the plant at the early stages leading to drying and withering. During the growth stage of a moong bean plant, major pests like leafhopper, aphids, whitefly affect the Green Gram crop. These pests can be controlled by spraying either Dimethoate or Phosphomidan, Mehyldematan @ 2 ml per liter of water.
Read: Button Mushroom Cultivation.
During the growth stages of this crop, the yellow mosaic disease can be observed. The impacted plants show yellow mottled symptoms. These plants can be destroyed when they appear on the plants. Leaf curl diseases and leaf crinkle also found to damage the crop. Remove this kind of plants as soon as they appear. Apart from these diseases this crop is also affected by wilt, root rot which has to be destroyed & the impacted area can be controlled by spraying with 0.1 % Bavistin solution. The Powdery mildew and Cercospora can be controlled with a spray of 1% solution of Bavistin.
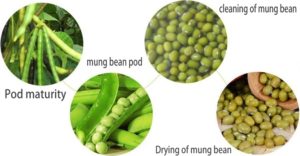
Harvesting of Green Gram:
The best time to harvest the crop, when 85% of the pods are fully matured. Avoid harvesting in bad weather condition and keep the harvested stack for drying in the field after cutting on the threshing floor. Remove any admixtures before the start of harvesting.
The yield of Green Gram:
Green Gram yield depends on the seed and farm management practices, at an average of 10 to 14 quintals/hectare can be expected.
Read: Summer Gardening Tips, Ideas.
Amazing Facts About Green Gram.