Introduction to RAS fish farming
The following information about RAS Fish Farming/Recirculating Aquaculture System.
Introduction:
Aquaculture is one of the fastest growing sectors in agriculture because of the growing demand for protein-rich food. Rearing fish in the farms is considered to be a profitable investment and is very popular. The most important reasons for fish farming or aquaculture are non-availability of wild fish due to over-harvesting and the contamination of natural water bodies. The traditional aquaculture industry has been facing several problems such as nonavailability of land, water resources, ecosystem imbalance, wastewater management, disease outbreaks, etc. One such effective solution to manage these problems is recirculating aquaculture system (RAS).
A technology for high-density farming of fish under controlled environmental conditions is termed as Recirculating aquaculture system. These are tank-based systems which use mechanical and biological filters to farm any water species like fish, clams, shrimp, etc. The term recirculating is associated with these systems because the water in the fish tanks is reused after being treated. These systems are sustainable as they use almost 90-99% less water than the traditional aquaculture methods. These recirculating systems are expected to reduce the waste discharge, need for chemicals and escape of fish and parasites. Mostly RAS is designed for freshwater environments and are considered to be costly. Controlling all the critical parameters required for the system is an important and necessary component and should be monitored regularly. Unlike traditional aquaculture farms, which are dependent on external environmental patterns, these recirculating systems either partially or completely eliminate the need for external factors and this depends greatly on the construction and functioning of the system. Deploying these systems need knowledge, expertise, and persistence for proper functioning and successful results.
Benefits associated with RAS fish farming
Recirculating aquaculture systems offer a range of advantages over traditional techniques such as;
- Maximum production
- Less water and land requirement
- Complete control of environmental parameters
- Easy growing and harvesting
- Effective disease control
- Flexible to rear any fish variety
- Can be located close to market areas
- Production is possible all year round
- Less pollution or contamination of water
Recirculating aquaculture system design for RAS fish farming
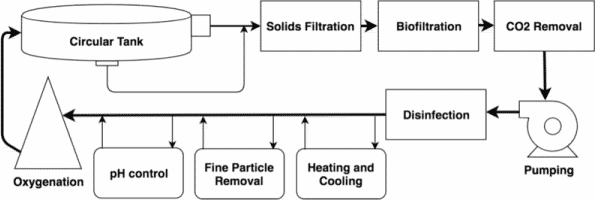
The basic system has a simple design and consists of fish tanks, mechanical filter, biofilter, trickling filter or degasser, oxygen enrichment unit, UV disinfector. Some extra facilities like the pH regulator, heat exchange unit, denitrification unit can be added to the design depending on the requirements.
The basic operating principle of these systems is that the water from the fish tank moves through the mechanical filter and then through the biological filter; the water is stripped of carbon dioxide before getting aerated and is returned back to the fish tanks.
Fish tanks of RAS fish farming
Tanks for aquaculture or fish farming in these systems can be of any shape and size like rectangular, circular, oval, etc. Mostly circular or oval tanks are preferred because they are easier to clean and facilitate easy water circulation when compared to rectangular tanks. Rectangular tanks are generally used on inclined areas. The size of a fish rearing tank may range from 500 to 500K gallons capacity and this depends on the factors like type of fish, stock rate, water requirement, and quality. The tank should be built such that it is compatible with other components of the system. The materials required to build the tank can be metal, wood, glass, rubber, concrete or plastic. Any material which is non-toxic and doesn’t corrode can be used for constructing the tank. The inner surface of the tank should be clean and smooth. Each and every material used for this purpose has its own advantages and disadvantages. The inclination of the fish tank can help to drain easier but has little or no effect on self-cleaning ability.
Most modern tanks are being constructed with outlets that have optimal waste removal capacity and are fitted with suitable mesh screens. These outlets should also make removal of dead fish easy. Some tanks are also fitted with sensors to detect the water level, oxygen content, temperature, etc. so that they can be controlled automatically. Tanks should also have diffusers for a sufficient supply of oxygen.
Other than circular and rectangular tanks, there is one more variety called the raceway tank which is a blend of circular and rectangular shapes. These tanks have a wall in the center to facilitate circulation.
Pumps and flow of water of RAS fish farming
In recirculating aquaculture systems, there should be a constant flow of water and there should be a possibility to alter the speed, pressure, and direction depending on one’s requirement. The movement of water is controlled through gravitation and before it is used in the system, it is generally pumped to an elevation from where it begins to flow.
The most common type of pump used in RAS is a centrifugal pump which operates from the thrust generated by the spinning of water at a high speed in the pump head. The pump is usually placed outside the tank and operates at high pressure. A pump with high flow and low lift capacity is chosen to minimize energy consumption. Earlier centrifugal pumps had a recirculating pressure of 25 ft, but now the pressure is about 10 ft. Two other types of pumping arrangements are axial and airlift pumps.

Mechanical filters of RAS fish farming
A practical way of removing the waste from the fish tank is possible through mechanical filtration. Modern recirculating systems have an outlet with a filter called the micro screen of mesh size 40 to 100 microns. The presence of the micro screen has some advantages such as it reduces the load on biofilter, removes the organic impurities, improves or facilitates the Biofiltration process. The type of micro screen used is called a drum filter and has the following functions:
- Filters the elements present in the water
- The elements are pushed to the backwash area by the rotation of the drum
- The solid waste is removed into the sludge tray by spraying water on the filter
- The sludge is removed with water from the tank and is sent to external waste treatment
Biofilters of RAS fish farming
This is the most important component of RAS because it helps in removing the fine pollutants from water during waste treatment. The media within the filter is made up of materials like plastic sheets, beads, lava rock, gravel or sand grains. The properties of the media should be such that it should have a high surface area for bacterial growth, pores for movement of water, clog resistant and should be easy to clean.
A simple biofilter can be a wheel, barrel or box filled with media on which nitrifying bacteria grow. It can be made of plastic, wood, glass, metal or concrete. The size of the biofilter defines the fish carrying capacity of the entire system. The surface area of the filter should be large so as to accommodate high-density bacteria to process loads of waste present in the fish tank. While designing biofilters the surface area, ammonia loading and hydraulic loading should be properly estimated. These filters can be configured in many ways and two major categories of biofilters are:
- Submerged bed filters – they need aeration before and after the water passes through them
- Emerged bed filters – the filters have constant oxygen supply to support the process and are of two types:
- Trickling filters
- Rotating biological contractors
Biofiltration can be effectively done only if the temperature and pH level of the water is regulated properly. The minimum temperature of the water should be in between 10-35˚C and the pH range should be around 7 to 8. High and low pH may result in inefficiency of the filter and higher toxic effect respectively. So a balance is highly important and this depends on two factors; the biological activity of the filter and the amount of CO₂ produced in the tank and the nitrification process.
Sump for waste collection in RAS fish farming
The presence of waste in the tank increases the demand for oxygen and decreases the amount of dissolved oxygen content in water, thereby lowering the density of fish in the tank. A Sump or a clarifier tank is used to collect the excess waste at a slow rate. The main idea of the sump is to collect and sediment all the solid waste which could otherwise block the biofilter and use up the oxygen. This is isolated from a fish tank and should be periodically cleared. The shape of the sump should be ‘V’, so as to facilitate easy cleaning.
Degassing of RAS fish farming
Accumulated gases in the fish tank should be cleared by providing proper aeration and this method is called stripping. Respiration of fish produces carbon dioxide and bacteria in the biofilter produces nitrogen, both of these are harmful to the growth of the fish. If it is a saltwater tank, then there is a chance of hydrogen sulphide production, which is equally toxic to the fish. Supplying air into the tanks can drive the gases away through turbulence. A trickling filter system is often used for this process. When water is made to flush down from the top of the filter through the plastic media stacked in a column it increases turbulence and contact which helps in stripping the gases.
Aeration or oxygenation in RAS fish farming
Providing oxygen supply to the water in the tanks is called aeration. Warm and cool water recirculating systems need 6 and 8 ppm of oxygen respectively for bacteria and fish to survive. RAS tanks which have high load carrying capacity should be able to replace oxygen every 20 or 30 minutes. There should be proper and regular supply of oxygen otherwise it could lead to loss of fish and also there should be a backup arrangement for large recirculating systems. Blowing air through a submerged air stone is the commonly used method to aerate the tank. For one pound of food supplied to the fish, the amount of air required is around 187 lpm/kg/day approximately. Diffuser hose and airlifts are devices used for the aeration process. When aeration is provided sufficiently then there is no need for a distinct carbon dioxide stripping unit.
Types of wastes in RAS fish farming
The solid wastes present in the tank can be categorized into three types and their removal methods are listed here:
Settleable wastes
- Removed into a sump
- Some wastes can be removed from the surface depending on the flow rate
- Can also be removed by suspending them in an exterior settling tank
- The modern way of removal is ECO-TRAPTM which uses a plate at the bottom of the tank to separate the wastes
Suspended and dissolved wastes
- Needs screen filters or media filters to remove wastes
- Rotating micro screens, foam fractionation, floating bed filters, Biofiltration, moving bed filters, etc. are some techniques to remove wastes
Ammonia and nitrate toxins
- Occur in two forms; ammonium (ionized) and free ammonia
- Sometimes also present in the form of ammonia nitrate
- Nitrite concentration should be below 0.5 mg/l
- Can cause brown blood disease in the fish
- Can be prevented by adding 1 pound of salt to 120 gallons of water
- Ammonia loading depends on the biomass of fish in the tank or the weight of feed
- Roughly 25 mg of ammonia is produced for every 100 g of fish in the tank
- Excess ammonia can be eliminated by adding fresh water, reducing feed and density of fish in the tank
Nitrification of RAS fish farming
The process of detoxifying ammonia is called nitrification. Converting ammonia nitrogen to less toxic nitrogen dioxide and finally to non-toxic nitrate through bacterial action is the principle of nitrification. The bacterium has to be grown on a surface for this process to occur and clean water with normal temperature should be used. The bacteria required for this process are of two types; one that converts ammonia to nitrogen dioxide is called the ‘nitrosomonas bacteria’ and the other which converts nitrogen dioxide to nitrate is called the ‘nitrobacter bacteria’. The entire process of nitrification is aerobic in nature that it requires oxygen to occur. The minimum amount of oxygen required to convert 1 mg of ammonia is around 5 mg. Also for the bacteria to survive an additional 5 mg of oxygen is required. It is important to note that for this process to occur in large tanks with a high density of fish and heavy ammonia content, the amount of oxygen required is also extremely high and should be supplied before and after the Biofiltration process.
De-nitrification
The end product of the nitrification process is nitrate and is non-toxic in nature, but the presence of nitrate beyond 100 mg/l has a negative impact on the growth of fish and feed conversion. Supplying fresh water regularly to the tank can keep the levels of nitrate low, but the main aim of recirculating systems is to maintain or lower the water consumption rate (save water resource), therefore a process called de-nitrification is adopted. This process is required if the supply of water is less than 300 liters per kg of feed. The bacteria used for this process is called the de-nitrifying bacteria and is named as ‘Pseudomonas’. The entire de-nitrification process is anaerobic in nature and involves the conversion of nitrate to atmospheric nitrogen. The nitrogen from water is released into the atmosphere and an organic source like wood alcohol or methanol should be added to the de-nitrification chamber. The minimum amount of methanol required to de-nitrify 1 kg of nitrogen is about 2.5 kgs. The de-nitrifying chamber is fitted to the biofilter with a residence time of 2 to 4 hours.
pH balance in RAS fish farming
For the fish to survive in the water tanks the pH of the water should be maintained within a tolerable limit and the suitable range of pH is known to be in between 6 to 9.5. Imbalance in the pH levels may occur due to acids produced by the nitrification process. The value of pH below 6 inhibits the nitrifying bacteria and they do not remove the toxic content. pH of the recirculating systems can be maintained by adding buffers like sodium bicarbonate and calcium bicarbonate.
Additional parameters for consideration in RAS fish farming
Other than the above-mentioned requirements, there could be some additional functionality of the recirculating systems which are important for large commercial practices.
Feed for the fish
Feed should be given to the fish for growth and activity. Fish take in oxygen for protein synthesis and produce carbon dioxide and ammonia as waste. Fish excrete undigested feed into the water and this results in suspended waste or organic waste. So, while maintaining a recirculating system, it is recommended that dry feed is to be given to the fish so that there are less pollution and disease occurrence in the tank. There should be a high feed utilization rate such that there are less waste content and a lower burden on water treatment systems. Therefore, before designing the recirculating system, the feed conversion rate should be carefully estimated and only suitable feed introduced so as to save money and unnecessary load on the filters.
Types of fish suitable for RAS fish farming
Recycled water is warmer than natural water and it is considered that cold water breeds like the salmon and trout are not very much suitable for rearing in these systems. Species that can be grown in RAS are African catfish, barramundi, carps, perch, tilapia, pangasius, white fish, Atlantic cod, bluefin tuna, rainbow trout, sturgeon, seabass etc.
Managing the fish stock in RAS fish farming
It is important to keep the production of fish in line with the capacity of the recirculating system. To avoid overloading of the system with heavy stock density, many techniques are used.
- Fingerlings are not grown to market size fish in the same tank.
- Fish grown to an intermediate size are graded and moved to another tank
- Quarantine tanks are used for fingerlings before introducing them into growth system tanks
- The quarantine tank and growth tank are physically isolated
- 3 to 6 weeks of time is required to check and treat the fingerlings for any disease or infection in these quarantine tanks
Disinfection using UV light in RAS fish farming
The UV light can be used at certain wavelengths to destroy the DNA of biological organisms. Infection-causing single-celled pathogenic bacteria is targeted using UV light in recirculating systems. This method of treatment is done outside the fish tank and is not a suitable method for traditional fish farms where the bacteria can grow very fast. This technique works best when combined with mechanical and biological filtration methods. The number of UV rays can be expressed in terms of microwatt-seconds per sq cm (µWs/cm²). UV light required for disinfecting the water in the tank is estimated to be around 2000-10000 µWs/cm² for bacteria, 10K-100K µWs/cm² for fungi and 50K-200K µWs/cm² for parasites. It is worthy to note that UV light should be passed inside the water and not through lamps fitted outside the tank.
Ozone is an alternate to UV treatment method but is rarely used because over-dosing can cause injury and death of fish. Micro bacteria and unwanted organisms are targeted especially in hatcheries and fry production units because these small fish are more sensitive to such bacteria. Efficient handling of the system is important to get positive and safe results.
Foam fractionation of RAS fish farming
Surfactants i.e. chemicals having a molecular end are removed through this technique. These chemicals are a result of the protein degradation process and cause foaming problems in the tanks. Foam fractionation can sometimes remove fine solids and dissolved organic wastes. This technique is better suited for saltwater systems with salinity more than 12 ppm, such that air bubbles can easily be formed and foam production is dependable. Foam fractionator consists of a PVC pipe and an air stone. Commercial foam fractionator designs have fabrication done with acrylic columns. Two important things that get affected by the design of the fractionator are bubble size and time of contact between the air bubbles and dissolved organic substances.
Heating
Heat to the recirculating systems can be made available in two ways; either by heating the air space or by heating water. The area or building should have proper insulation and a proper water vapor condensing structure. Water vapor when condensed within the building can cause damage to the parts of the building. Direct heating is avoided because of scaling issues with hard water usage. So as a substitute polypropylene heating coils are connected to a boiler and water is heated. The temperature of the boiler is automatically controlled.
Centralized heaters are used to heat the space above the tanks. All calculations for humidity and carbon dioxide levels should be carefully considered before deploying this method.
Greenhouse technology can also be an alternate solution for setting up recirculating aquaculture systems.
Monitoring and control of RAS fish farming
Fish farming can be properly done only if there are a regulated control and monitoring system within the RAS. A central system to control and monitoring of certain features like oxygen levels, pH range, water levels, and other functions is deployed for efficient handling of the systems. Automatic sensors or alarms installed in these systems can indicate when a problem arises. Even though the systems operate automatically, they need to be monitored regularly by skilled personnel such that there is a negligible loss. In case of Emergency, pure oxygen back up is a must to have in the production area. A generator to supplement electrical supply is also required for efficient handling of the RAS.
Very comprehensive. Thanks for making it available online.
You welcome.
Need the name of the company who will provide RAS (Recycled aquaculture system).
Dear Sir
I am from Dhule maharashtra and I am willing to start a RAS system fishery unit at Dhule city , sir in our local area we get a small fish hard 25 to 30 grams weight.we call them as murre. I want to grow that breed in RAS system fishery unit would you please guide me.
Thankyou
Dear Sir , I want to know the name of the company who provides the Ras (recirculating acquaculture system)… I’m from odisha,khordha,balakati.
Dear blogger you content about RAS Fishing was excellent and knowledgeable…thanks and Please provide us recirculating acqaculture system (RAS ) fishing details project report and critical information regarding this and also let’s us know where to contact for machines and equipment reliable dealers of India or other… please please please sir….for this we will be grateful to you forever
Wants to know about fish farming or poultry farming.
Read: Poultry Farming.
Read: Fish Farming.
Hello your information is very much used full.
I am planning for RAS Setup in south India doing some ground work on it also gathering quotes (from 10 to 12 tons capacity) from the RAS providers can you communicate with me over an email and appreciated if you can send more info and quotes as per the above mentioned capacity.
Dear sir
i am from chennai and i would like to start a fish farming with RAS syatem , can you provide the name of the company that provide RAS machines and equipment reliable dealers.
I would like to start a fish farming with RAS system, and I would like to know the companies that provide and install RAS equipment.
Hello sir,
I want to RAS fish farming in Himachal Pradesh. But I don’t know much about it. I have so many questions about this business. But basic q. Is it suitable in my state.
2. Cost of setup unit.
3. Have any subsidy?
4. Expenses for seed, feed
5. Companies that set up the RAS unit
6. Market to sell fish. etc.
Thanks
Sir,
Please send me the duration of training and complete project report,
Sir,I am Ramanatha Reddy.i am in Kadapa district. Sir unit wise cost quotation please