Soil Types and Suitable Crops in India:
Introduction to Soil Types:- The following information is all about soils and their types in India. It also explains suitable crops for different soil types as well as areas of these soils.
- What is Soil: A soil can be defined as the outermost layer of the earth’s crust which plays a major role in growing food and trees. It contains organisms and also consists of minerals, organic matter (humus), water, gases, and air.
- Soil Formation: How the soil formed? well, soil formation is a very long process and actually begins with the weathering of rocks into small fragments. The origin of soil is from rocks (parent material), usually formed when rocks are exposed to the atmosphere in the process of physical and chemical decomposition. Parent material (usually rocks) and the process of soil formation decide the soil properties. The soils in India are divided into 2 broad categories based on their formation.
- Residual Soils
- Transported Soils.
- Soil Types – Factors that Determines (Affect) Soil Formation: There are some factors that determine the types of soil found in India.
- Topography.
- Climate.
- Parent materials (usually rocks).
- Organisms.
- Time.
- Soil Types – Soil Profile and Horizon: As we know soils are made of layers which are also called “Horizons”. These all layers (horizons) put together to form a soil profile. The soil profile indicates the complete history of soil formation and its ingredients of it. In general, a soil profile consists of 6 horizons.
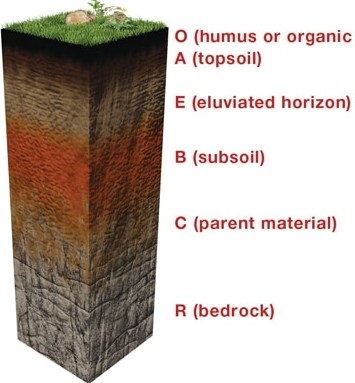
- O (Organic or humus).
- A (Top Soil).
- E (Eluviated layer or Exit layer).
- B (Subsoil).
- C (Parent material (from which soil is formed)).
- R (Bedrock).
- Soil Types – Soil Minerals: The soil consists of primary and secondary minerals.
- Primary Minerals – Calcium, Sodium, Aluminium, Magnesium, and Iron.
- Secondary Minerals – Clay and Mineral Oxides.
- Soil Types – Functions of Soil: Well, soil plays a major role and has primary functions in the earth’s life.
- Soil works as a medium for plant growth in the ecosystem.
- Soil can able store, purify and supply water to the needy.
- Soil is considered as a modifier of Earth’s atmosphere (climate).
- Soil has natural habitat and basis for life survival.
Soil Types in India:- There are many soil types that exist in the Indian continent. Each soil type has specific characteristics and suitable to grow only a certain type of crop.
- Soil Types – Alluvial Soils:

- Regions – You can find Alluvial soils in most part of the delta regions of Northern India. This soil covers more than 35% of the total land in India.
- Characteristics – These soils are rich in nutrients like phosphoric acid and organic matter (humus). However, they are poor in nitrogen and potash. Alluvial soils are a mixture of clay and sand (loam). These soils tend to be sandier and can quick-draining properties than many other soils.
- Suitable Crops of Alluvial Soils – Tobacco, Cotton, Rice, Wheat, Bajra, Sorghum (Jowar), Pea, Pigeon pea, Chickpea, Black gram, Green gram, Soybean, Groundnut, Mustard, Linseed, Sesame, Barley, Jute, Maize, any Oilseeds, vegetables, and fruits are suitable in these soils under ideal irrigation.
- Soil Types – Black Soils:

- Regions – Black soils are also called Cotton soils or Regur Soils. These soils mainly found in the Deccan lava tract which includes the states of Telangana, Andhra Pradesh, Maharashtra, Tamil Nadu, Madhya Pradesh, and Gujarat. Mostly, you can find this type of soil in the river valley Godavari, Krishna, Narmada, and Tapi. Black soils are formed due to the weathering of the lava rocks.
- Characteristics – Black soils are rich in iron, lime, magnesium, and aluminum. However, they are poor in phosphorus, nitrogen, and humus (organic matter). Usually, this soil gets its black colour from various salts or from humus during soil formation. Black soils contain a large amount of clay but are sandy as well in hillier regions of the country. Black soils become sticky when wet and develop wide cracks during the dry season.
- Suitable Crops of Black Soils – The black soil moisture very well hence it’s excellent for growing cotton. This is also popularly known as black cotton soil. However, there are many other crops that can be grown in these soils are; Rice and sugarcane, wheat, Jowar, linseed, sunflower, cereal crops, citrus fruits, vegetables, tobacco, groundnut, any oilseed crops, and millets.
- Soil Types – Red and Yellow Soils:

- Regions – These soils are found in parts of Chhattisgarh, Deccan plateau, Orissa, and the Western Ghats.
- Characteristics – These soils are red in color due to the presence of iron oxide. These are formed due weathering of metamorphic rocks. These soils are sandy and somewhat acidic and rich in potash. However, they are very poor in lime, nitrogen, phosphorous, magnesium, organic matter (humus).
- Suitable Crops of Red and Yellow Soils – Rice, wheat, sugarcane, maize/corn, groundnut, ragi (finger millet) and potato, oilseeds, pulses, millets, and fruits such as mango, orange, citrus, and vegetables can be grown under ideal irrigation.
- Soil Types – Laterite Soils:

- Regions – Tamil Nadu, Karnataka, Kerala, Madhya Pradesh, Orissa, and Assam.
- Characteristics – These soils acidic in nature and are poor in humus (organic matter), phosphate, nitrogen, and calcium. Laterite soils are very rich in iron.
- Suitable Crops of Laterite Soils – These soil are not very fertile and are used in cotton growing, rice cultivation, wheat cultivation, pulses growing, cultivation of tea, growing coffee, growing rubber, growing coconut, and growing cashews. Most of the time this soil is used to make bricks due to the presence of large amounts of iron.
- Soil Types – Arid Soils:

- Regions – West of the Aravalli.
- Characteristics – Arid soils are sandy and have low clay content. These soils are deficient in humus and moisture due to the fact that high evaporation in arid regions. Arid soils are saline in nature due to the high salt content and poor nitrogen. However, they are rich in plant food. The colour of Arid soils ranges from red to brown.
- Suitable Crops of Arid Soils – You can grow any drought and saline-tolerant crops such as wheat, cotton, corn (maize), millets, pulses, and barley.
- Soil Types – Forest and Mountain Soils:
In case if you miss this: How To Grow Coriander Organically.

- Regions – One can find this type of soil Himalayan region, Western and Eastern Ghats, and some parts of the peninsular plateau.
- Characteristics – This type of soil are rich in organic matter(humus) but are poor in nutrients such as potash, phosphorus, and lime. These soils are somewhat acidic in nature. Crops cultivated in these soils require supplementing the good fertilizers.
- Suitable Crops of Forest and Mountain Soils – These soils are good for cultivating tea, spices, wheat, maize, barley, coffee and tropical fruits, and temperate fruits.
- Desert Soils: These soils are sandy and dry and contain some amounts of nitrogen that are suitable for agriculture with good irrigation facilities. Generally, only drought-resistant crops like millet and barley can grow in these soils.
- Other Soils:
- Saline and Alkaline Soils: These soils are too low in nutrients and too high in salt for productive agriculture.
- Marshy and Peaty Soils: Marsh soils are not suitable for crop cultivation due to their high acidic nature. Peaty soils have high salt content and good organic matter (humus). However, they are deficient in nutrients like potash and phosphate. Mostly found in Kerala.
Soil Erosion and Its Impacts: Soil erosion is nothing but washing out the top layer (horizon) of soil which has more nutrients and organic matter (humus) required to maintain the ecosystem. There are many reasons for this soil erosion. Some of the natural causes are flooding, heavy rains, ice forming. Other mane made reason include, ploughing, Shifting cultivation, Deforestation, and Overgrazing. Soil erosion results in the following.
- Water holding capacity is reduced.
- Loss of nutrients.
- Reduces water infiltration (makes the soil harder).
- It does not remove topsoil uniformly, hence not possible to apply fertilizers and chemicals uniformly in the topsoil.
Protecting from Soil Erosion: It’s our responsibility to save the ecosystem from soil erosion.
We can achieve soil conservation through the following.
- Changing agriculture/farming practices.
- Checking to overgraze.
Note: Crop growers can prevent soil erosion by providing muck material at the plant basin. Mulch materials like hay, dried leaves can be used. Nowadays, there are plastic mulch materials are available in the market.
Soil Testing and its Need: A soil test is performed to analyze soil samples to determine nutrient content, composition, and other characteristics such as acidity or pH level. Commercial crop growers should adopt this practice before starting a plantation. This soil test allows determining the nutrients and micro-nutrient deficiencies so that farmers can supplement these nutrients to make the soil fertile. Based on soil test results, farmers can choose appropriate manures and fertilizers for better crop yields. For measuring soil pH, farmers can buy soil pH meters and check soil acidic levels. This meter is also helpful, especially for indoor gardening, container gardening, greenhouse/Polyhouse farming.
In case if you are interested in this: Hydroponic Nutrient Chart.
- Economical Aquaculture: A Guide to Low-Budget Fish Farming
- 15 Common Planting Errors That Can Doom Your Fruit Trees
- How to Make Houseplants Bushy: Effective Tips and Ideas
- Innovative Strategies for Boosting Coconut Pollination and Yield
- Pollination Strategies for Maximum Pumpkin Yield
- The Complete Guide to Chicken Fattening: Strategies for Maximum Growth
- Natural Solutions for Tulip Problems: 100% Effective Remedies for Leaf and Bulb-Related Issues
- Revolutionizing Citrus Preservation: Towards a Healthier, Greener Future
- Natural Solutions for Peony Leaf and Flower Problems: 100% Effective Remedies
- Maximizing Profits with Avocado Contract Farming in India: A Comprehensive Guide
- Natural Solutions for Hydrangea Problems: 100% Effective Remedies for Leaf and Flowers
- The Ultimate Guide to Choosing the Perfect Foliage Friend: Bringing Life Indoors
- From Sunlight to Sustainability: 15 Ways to Use Solar Technology in Agriculture
- The Ultimate Guide to Dong Tao Chicken: Exploring from History to Raising
- The Eco-Friendly Makeover: How to Convert Your Unused Swimming Pool into a Fish Pond
- Mastering the Art of Delaware Chicken Farming: Essentials for Healthy Backyard Flocks
- 20 Best Homemade Fertilizers for Money Plant: DIY Recipes and Application Methods
- How to Craft a Comprehensive Free-Range Chicken Farming Business Plan
- Brighten Your Flock: Raising Easter Egger Chickens for Beauty and Bounty
- How to Optimize Your Poultry Egg Farm Business Plan with These Strategies
- Subsidy for Spirulina Cultivation: How Indian Government Schemes Encouraging Spirulina Farmers
- Ultimate Guide to Raising Dominique Chickens: Breeding, Feeding, Egg-Production, and Care
- Mastering the Art of Raising Jersey Giant Chickens: Care, Feeding, and More
- Ultimate Guide to Raising Legbar Chickens: Breeding, Farming Practices, Diet, Egg-Production
- How to Raise Welsummer Chickens: A Comprehensive Guide for Beginners
- How to Protect Indoor Plants in Winter: A Comprehensive Guide
- Ultimate Guide to Grow Bag Gardening: Tips, Tricks, and Planting Ideas for Urban Gardeners
Alluvial soil are rich in potash but low content of phosphorus.