Aquaponics, a sustainable gardening method, combines aquaculture and hydroponics to create a self-sustaining ecosystem in your garden. This blog will explore 15 DIY aquaponic plans anyone can build. These systems efficiently grow plants and fish, making them perfect for eco-conscious gardeners.

15 DIY Aquaponic Plans You Can Build in Your Garden
DIY Aquaponics Garden Tower: A Step-by-Step Guide
This vertical garden system efficiently utilizes a 50-gallon tank filled with water and fish, like tilapia. The fish waste contains ammonia, converted by beneficial bacteria into nitrates. These nitrates serve as a nutrient-rich fertilizer for plants. You can grow various veggies, herbs, and small fruit trees in the vertical tower. Water from the tank is pumped to the top of the tower, allowing it to trickle down and nourish the plants. This method conserves water and space, making it an excellent choice for home gardeners.
How to Build a Simple Aquaponics System with a 5-Gallon Bucket
Materials and Tools Needed
- A 5-gallon bucket with a lid
- A small water pump (about 100 GPH)
- 3/4-inch PVC pipe
- A 1/2-inch PVC pipe
- A 3/4-inch to 1/2-inch PVC reducer
- A 1/2-inch PVC elbow
- A 1/2-inch PVC tee
- A drill of 1/4 inch bit and a 1/2 inch bit
- A hacksaw
- A utility knife
- A marker
- Some aquarium silicone sealant
- Some zip ties
- Some gravel or clay pebbles
- Some plants (lettuce, herbs, etc.)
- Some fish (goldfish, guppies, etc.)
In case you missed it: Growing Vegetables and Fish Together in the Backyard: Starting a Backyard Aquaponics
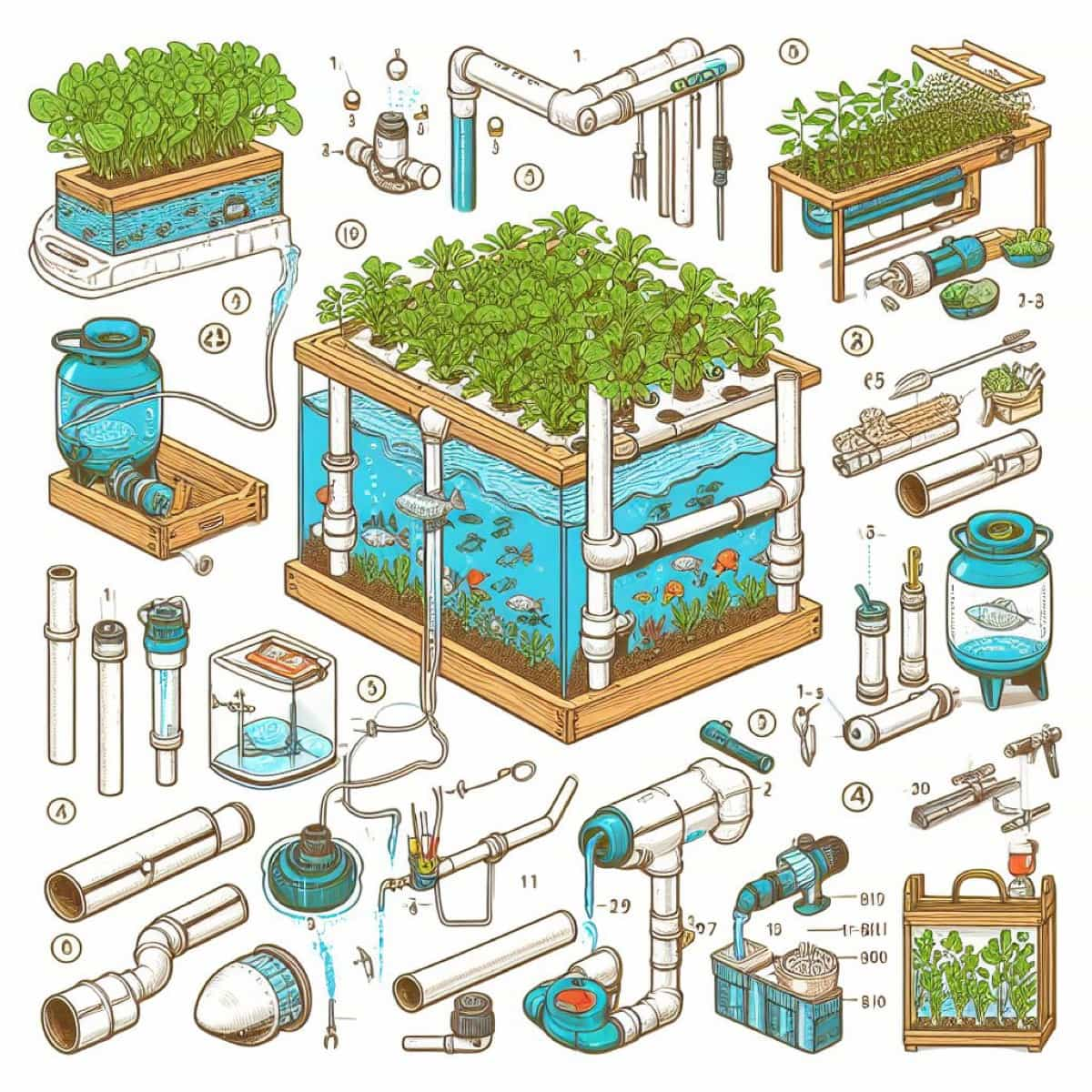
Building Process
- Cut a hole in the center of the bucket lid with the utility knife. The hole should be slightly smaller than the diameter of the 3/4 inch PVC pipe.
- Cut a piece of the 3/4 inch PVC pipe about 12 inches long. This will be the standpipe that will hold the plant grow bed above the water level.
- Make hole near the bottom of the standpipe with the 1/4 inch bit. This overflow hole will prevent the water from rising too high in the grow bed.
- Insert the standpipe through the hole in the bucket lid and secure it with silicone sealant. Make sure there is no gap between the pipe and the lid.
- Cut a piece of the 1/2 inch PVC pipe about 18 inches long. This will be the inlet pipe that will bring water from the pump to the grow bed.
- Attach the PVC reducer to one end of the inlet pipe and the PVC elbow to the other.
- Cut another piece of the 1/2 inch PVC pipe about 6 inches long. This will be the outlet pipe that will return water from the grow bed to the bucket.
- Attach the PVC tee to one end of the outlet pipe and another PVC elbow to the other end.
- Drill holes along the outlet pipe with the 1/2-inch bit. These holes will make water drain back into the bucket.
- Assemble the inlet and outlet pipes with the standpipe, as shown in the picture below. Use some silicone sealant to seal all the joints.
- Fill the bucket with water and plug in the pump. The pump should have a hose that fits over the reducer on the inlet pipe.
- Fill the space between the standpipe and the bucket lid with gravel or clay pebbles. This will be your plant grow bed where you can plant your seeds or seedlings.
- Add some fish to your bucket. Please ensure they are compatible with each other and your water temperature and pH level.
- You can harvest your plants when ready and feed your fish regularly.
Building a Small Aquaponics System Using PVC Pipe and Biofilter Media
Aquaponics is a sustainable method for growing food using fish waste and hydroponics. It combines fish farming with hydroponics, where fish waste provides nutrients for plants, and plants filter water for fish. To build a small aquaponics system, you need a fish tank, grow bed, PVC pipe, water pump, biofilter media, and your choice of fish and plants.
To build the system, cut PVC pipe to fit the dimensions of the fish tank and grow bed, drill holes for water spraying and aeration, fill the grow bed with biofilter media, and connect the pipes and fittings using PVC glue or silicone sealant. Plug the pump into the fish tank and allow water to circulate. Add fish and plants suitable for your climate and water conditions, such as tilapia, goldfish, lettuce, kale, basil, and mint.
In case you missed it: How to Grow Herbs in Aquaponics: Best Fish and Herbs for Creating Your Sustainable Aquaponic Garden
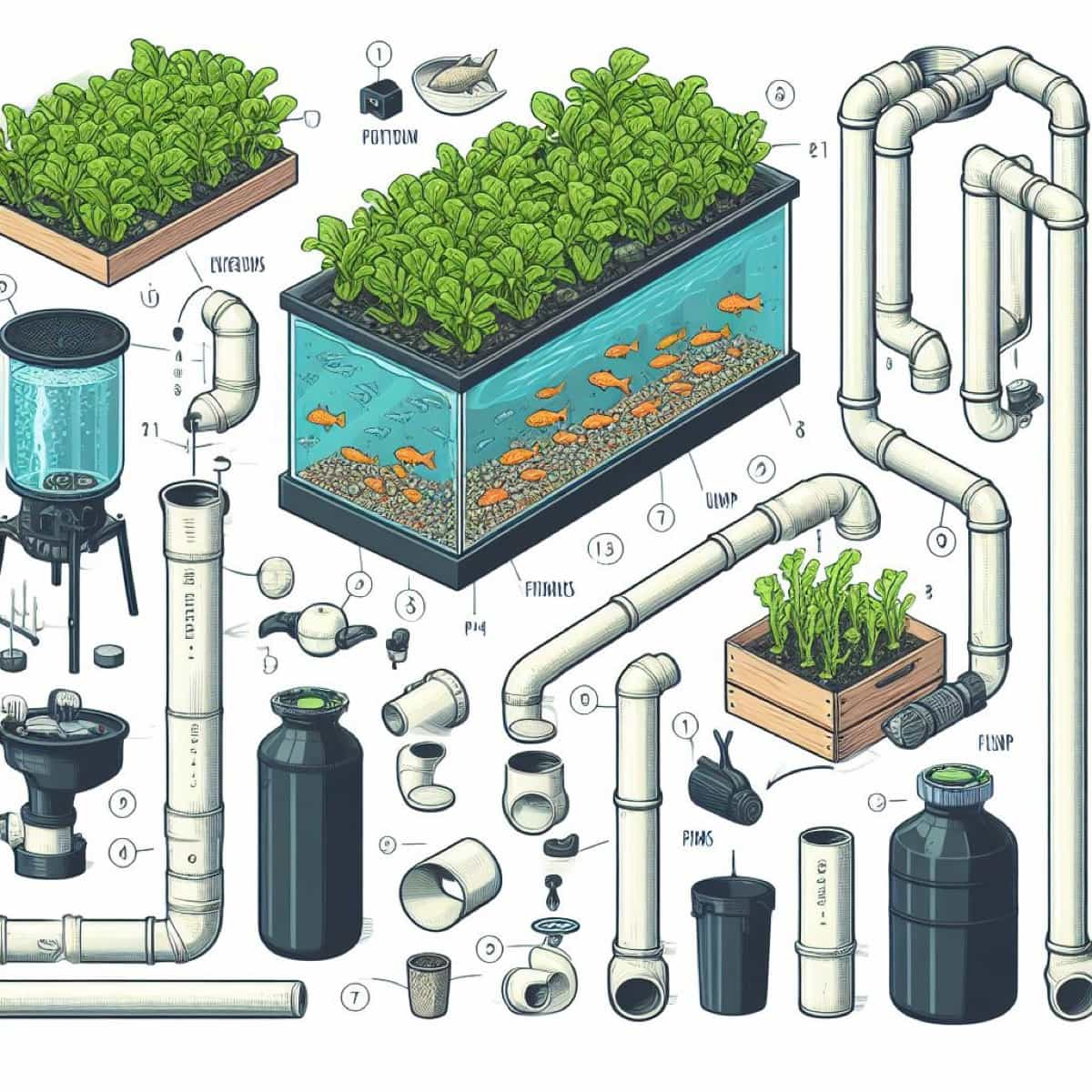
Monitor and maintain the system by checking water quality, adjusting pH, temperature, and ammonia levels, feeding fish according to their needs, and harvesting plants when ready. Enjoy food with a small aquaponics system using PVC pipe and biofilter media.
How to Create a Cost-Effective Aquaponics System Using IBC Totes and PVC Fittings
Aquaponics is a system that involves growing plants and fish together, using minimal resources and space. A cost-effective method is to use IBC totes and PVC fittings to create an aquaponics system. Cut one IBC tote into a fish tank and use the other half as a grow bed. Drill holes for drainage and fill with a suitable growing medium. Place the grow beds on the fish tank or a sturdy frame.
Connect the fish tank, grow beds, and a water pump using PVC fittings and pipes. Add a bell siphon or timer to control flooding and draining. Add fish and plants suitable for your climate and water conditions, such as tilapia or goldfish, and plants that grow well in water, like lettuce, herbs, or strawberries. Regularly monitor and maintain the aquaponics system, checking water quality, pH, temperature, and ammonia levels. Feed fish according to their needs and harvest plants when ready.
DIY Aquaponics Fish Tank: A Beginner’s Guide to Building and Cycling Your Fish Tank
To build and cycle your aquaponics fish tank, you need a 20-gallon tank, a grow bed, a water pump and tubing, a bell siphon or timer, growing media, and your choice of fish and plants. Place the tank in a location with adequate sunlight and electricity, cut a hole in the grow bed, connect the tubing to the pump and the grow bed, fill the grow bed with growing media, adjust the bell siphon or timer, and fill the tank with water.
In case you missed it: A Guide to Understand Aquaponics Farming: Check How this Guide Helps Beginners
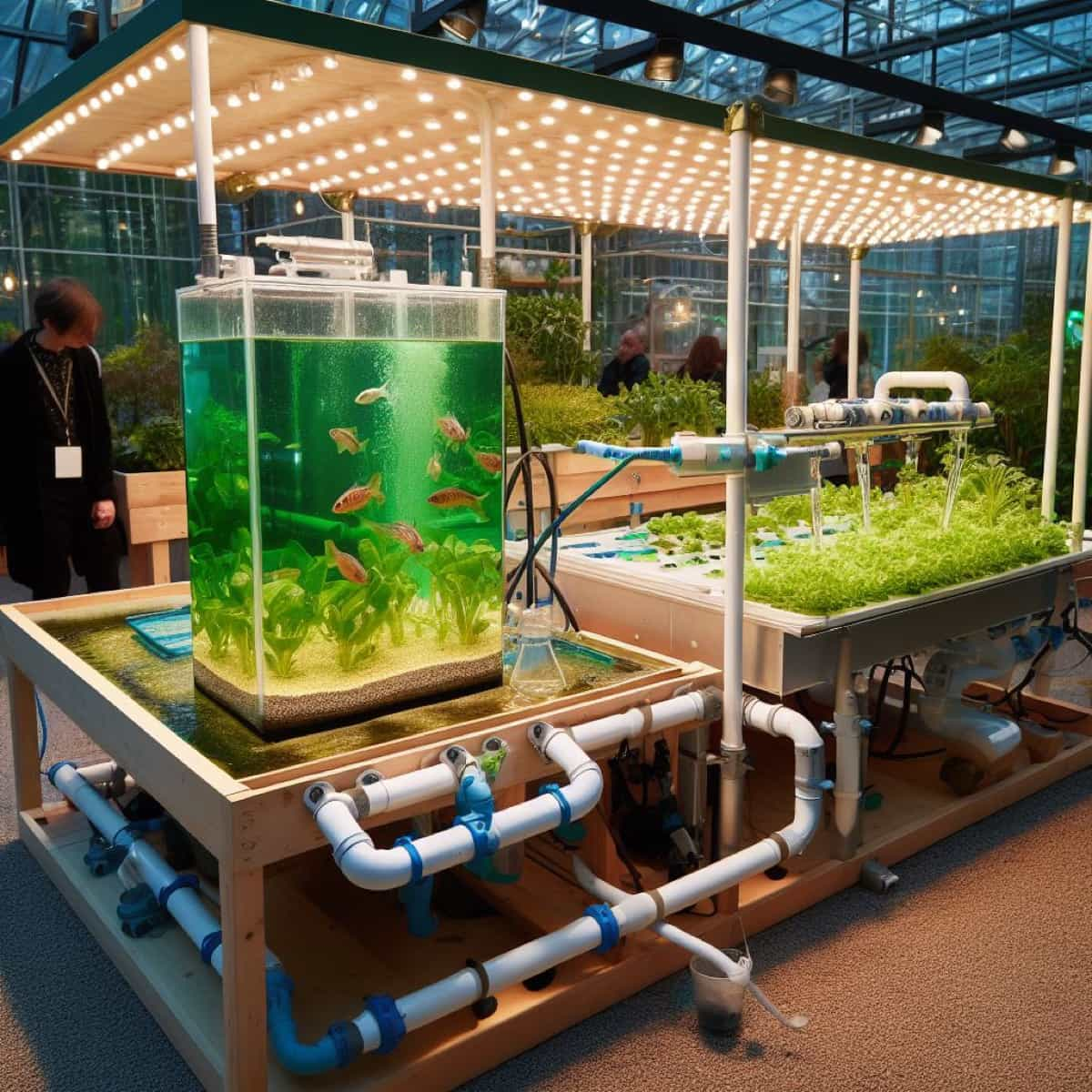

Cycling your fish tank involves establishing mutual bacteria that make convert ammonia from fish waste into nitrite and nitrate, which are less toxic for fish and usable by plants. Start cycling by adding fish food or a small amount of ammonia to the water, test the water daily with a test kit, and add fish gradually to avoid overloading the system. Add plants that suit your climate and preferences, such as leafy greens, herbs, or flowers.
Building an Aquaponics Greenhouse: Tips and Tricks for Success
- Choose a sunny spot for your aquaponics greenhouse to maximize natural light.
- Opt for hardy and fast-growing fish species like tilapia or catfish.
- Maintain a proper balance of fish to plants for optimal nutrient exchange.
- Invest in a good filtration system to keep the water clean and fish healthy.
- Regularly test and adjust the water’s pH to ensure it’s suitable for both fish and plants.
- Install heating and cooling systems to keep the greenhouse within the right temperature range.
- Pick plants that thrive in aquaponic systems, like lettuce, herbs, and tomatoes.
How to Make a DIY Aquaponics Grow Bed: Materials and Instructions
A DIY aquaponics grow bed can be created using a large plastic container, a drill with a hole saw attachment, a PVC pipe, a PVC elbow, a PVC end cap, a bulkhead fitting, a hose clamp, a water pump, gravel or clay pebbles, and plants of your choice. To create the bed, cut a hole in the container’s lid and insert the bulkhead fitting into the hole. Attach the hose to the bulkhead fitting and secure it with a hose clamp. Place the water pump in your fish tank.
Cut the PVC pipe into two pieces, attach the elbow to one end and the end cap to the other. Insert the longer pipe through the lid and position it above the fish tank. Fill the container with gravel or clay pebbles, leaving space for water. Plant your plants in the pebbles, ensuring their roots reach the water. Turn on the water pump and check for leaks or blockages. Enjoy your DIY aquaponics grow bed!
Creating a Vertical Aquaponics System for Maximum Space Efficiency
Aquaponics is a sustainable method for growing food in small spaces, combining fish farming and hydroponics. By stacking multiple grow beds on top of each other, you can increase yield without increasing your footprint. This vertical aquaponics system can be created using specific steps to maximize space efficiency and maximize yield without compromising on quality.
How to Build a DIY Aquaponics Fish Pump: A Step-by-Step Guide
This DIY aquaponics fish pump is a simple and effective way to grow fresh produce and fish. The process involves gathering materials such as a submersible water pump, PVC pipe, elbow, tee, cap, drill, hole saw, silicone sealant, zip ties, and hose clamps. The PVC pipe should be cut into three pieces, with one being 10 inches long, one 6 inches, and one 4 inches.
Drilling two holes on the 10-inch pipe, the holes should be slightly larger than the water pump’s outlet and inlet. The pump assembly should be inserted into the top and bottom holes of the pipe and secured with a hose clamp. The PVC elbow and tee should be attached to the pipe, and the cap should be secured to the tee.
In case you missed it: 7 Best Hydroponics Kits in India: Guide to Buy Top Hydroponics Kit at Affordable Price
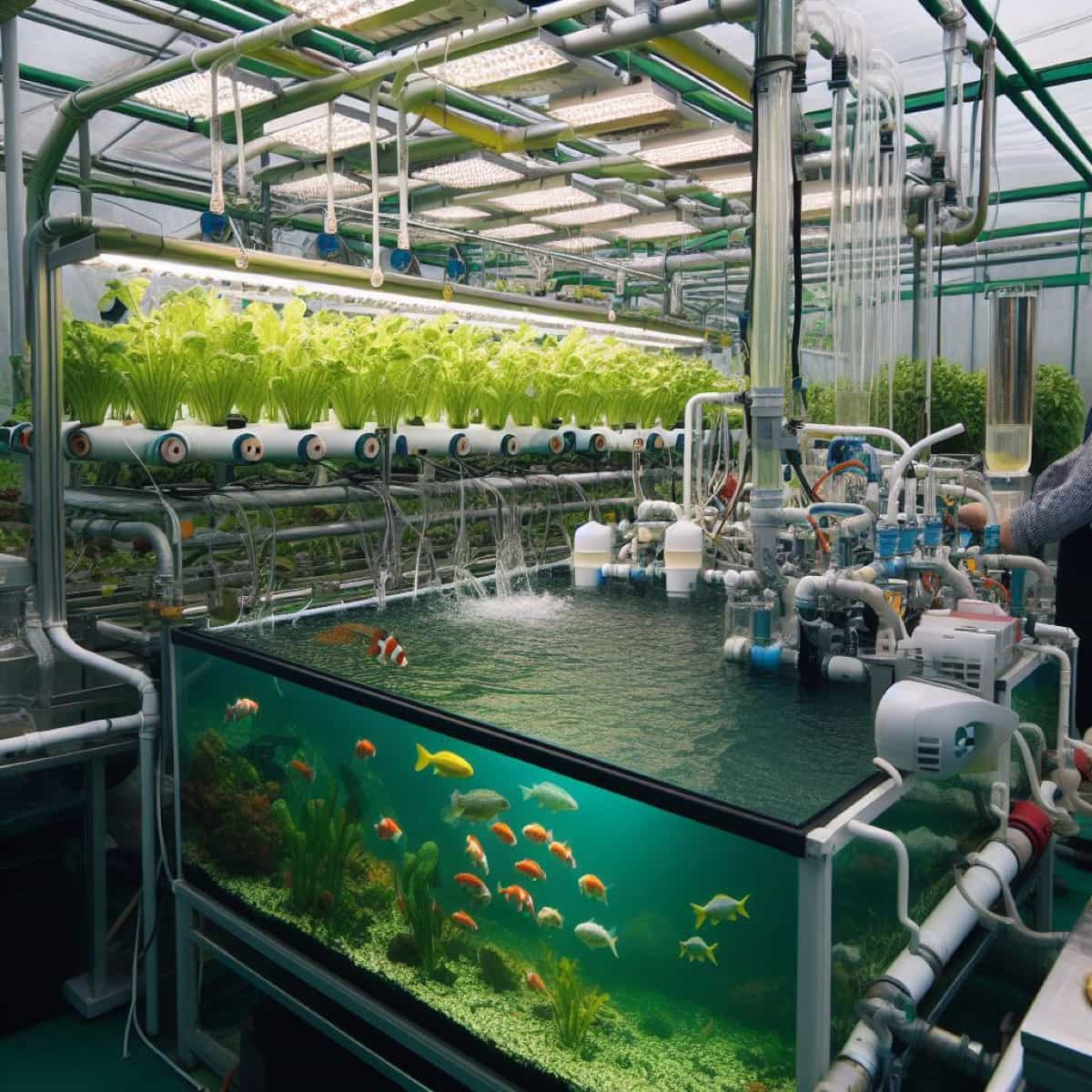

The pump assembly should be placed inside the fish tank and secured with zip ties. After testing the pump, it is important to check for leaks and blockages and adjust the flow rate according to the system’s needs. This DIY aquaponics fish pump is a great way to grow fresh produce and fish.
DIY Aquaponics Water Testing: Understanding pH, Ammonia, Nitrite, and Nitrate Levels
Aquaponics relies on maintaining pH, ammonia, nitrite, and nitrate levels to ensure the health and growth of fish, plants, and bacteria. The ideal pH range is 6-7, with 6.5 being optimal. To test pH, use a simple test kit or a digital meter. If the pH is too high or low, add natural buffers. Ammonia is toxic and can be reduced by adding plants, reducing fish feed, or performing partial water changes. Nitrite is toxic and interferes with oxygen transport, while high levels can lower fish’s immune system, increase disease risk, cause algae growth, and affect pH. Regular testing ensures a balanced and healthy aquaponics system.
Building a Modular Aquaponics System for Scalable Production
Modular aquaponics systems are a solution to the challenges of balancing fish and plant production, achieving optimal nutrient levels and economic returns, and scaling up to meet market demand without compromising system performance and stability. These systems consist of separate units for fish rearing, biofiltration, and plant growing, connected by pipes and pumps.
Each unit can be independently controlled and adjusted to achieve a desired output. Modular aquaponics offers several advantages over conventional systems, including flexibility, reduced risk of system failure, efficient use of space and energy, and easier monitoring and troubleshooting.
How to Build a DIY Aquaponics Aeration System: Using Air Pumps and Diffusers
This DIY aquaponics aeration system requires an air pump, tubing, check valve, T-connector, air stones, drill, and scissors. To create the system, drill holes in the grow bed or fish tank, cut tubing for the air pump, attach them to the T-connector and air stones, and connect the air pump to the check valve. Insert the T-connector into the check valve. Turn on the air pump and adjust the air stones to ensure even oxygen distribution. This system will create bubbles and oxygenate the water.
Creating a Closed-Loop Aquaponics System for Minimal Water Loss
Aquaponics uses less water than conventional agriculture, but some water loss occurs due to evaporation and transpiration. A closed-loop aquaponics system, which covers the fish tank and grow beds with transparent materials, traps moisture and reduces evaporation. This system saves water, increases production, and reduces pests and diseases.
In case you missed it: Pros and Cons of Wick Hydroponics: Ease of Setup to Limitations
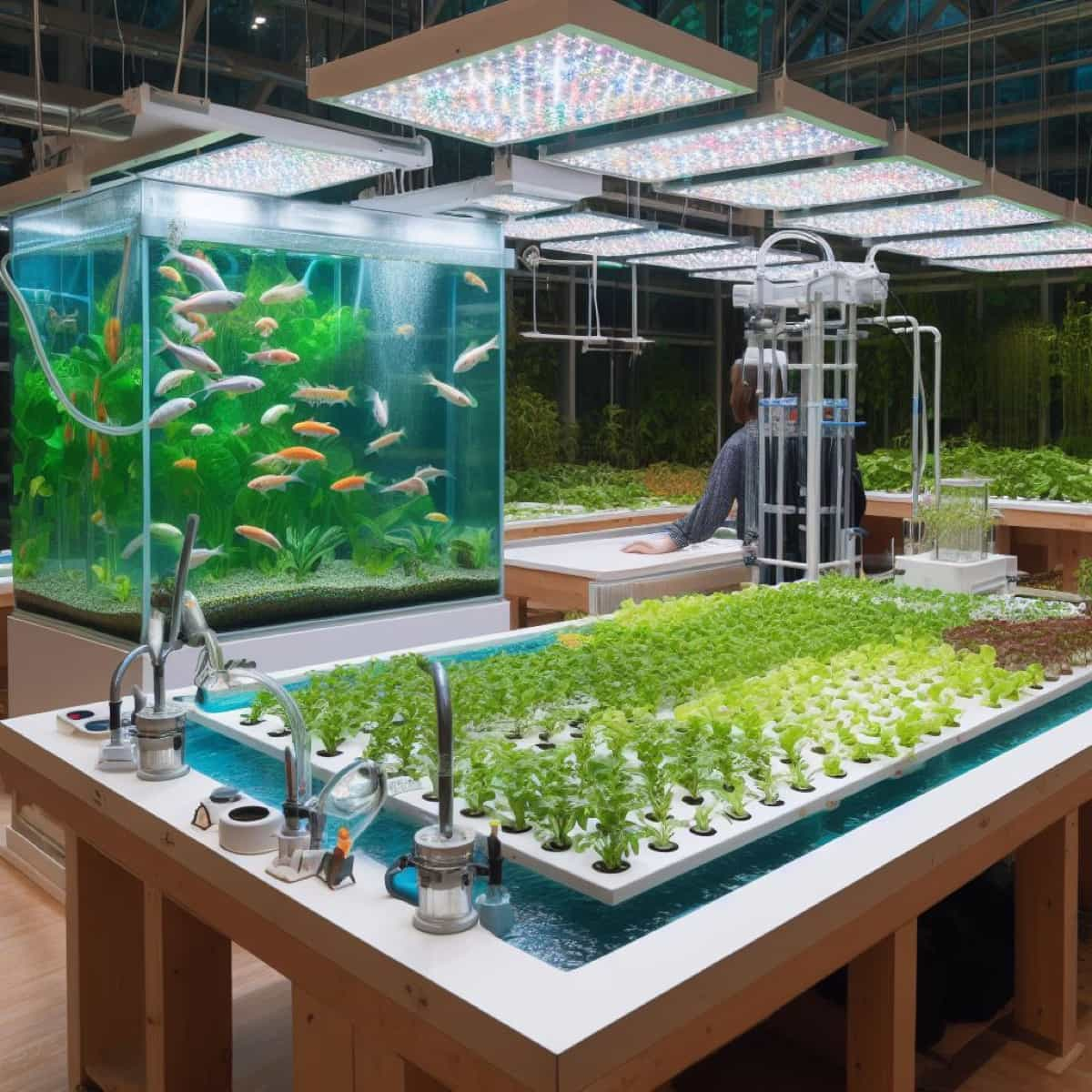

However, it requires careful monitoring and maintenance, including maintaining temperature, humidity, pH, ammonia, nitrite, and nitrate levels. To create a closed-loop aquaponics system, choose a suitable location, choose the right size and type of fish tank and grow beds, install a water pump and filter, fill grow beds with a growing medium, add fish, cover the system, and monitor regularly.
DIY Aquaponics Harvesting and Processing: Tips for Maximizing Your Crop Yield
DIY Aquaponics Harvesting and Processing method for growing fish and plants in a closed-loop system, using fish waste as fertilizer. Harvest fish when they reach the desired size and weight to maximize crop yield, handle them gently, and store them in a cooler with ice. Harvest plants when they are ripe and ready, wash them thoroughly, and preserve them by drying, freezing, or canning.
Process fish according to your preference, such as scaling, gutting, filleting, or smoking, or make fish stock, fish sauce, or fish fertilizer from bones and scraps. Process plants according to your recipe, such as chopping, slicing, dicing, or blending, and experiment with different flavors and combinations.
Building a Solar-Powered Aquaponics System for Off-Grid Production
A solar-powered aquaponics system is a sustainable and self-reliant way to grow food and fish. This method combines aquaculture and hydroponics, recycling water and nutrients. The system uses solar panels to power pumps, filters, and aerators, allowing it to be set up in any location with enough sunlight without relying on the grid or fossil fuels.
To build a solar-powered aquaponics system, you need a large fish tank or pond, a grow bed filled with gravel or clay pellets, a water pump, a solar panel, a charge controller, a battery, a DC-to-AC inverter, an air pump, an air stone, PVC pipes, and fittings, a drill, saw, tape measure, level, and marker.
In case you missed it: Different Types of Growing Mediums for DWC: Deep Water Culture Hydroponics
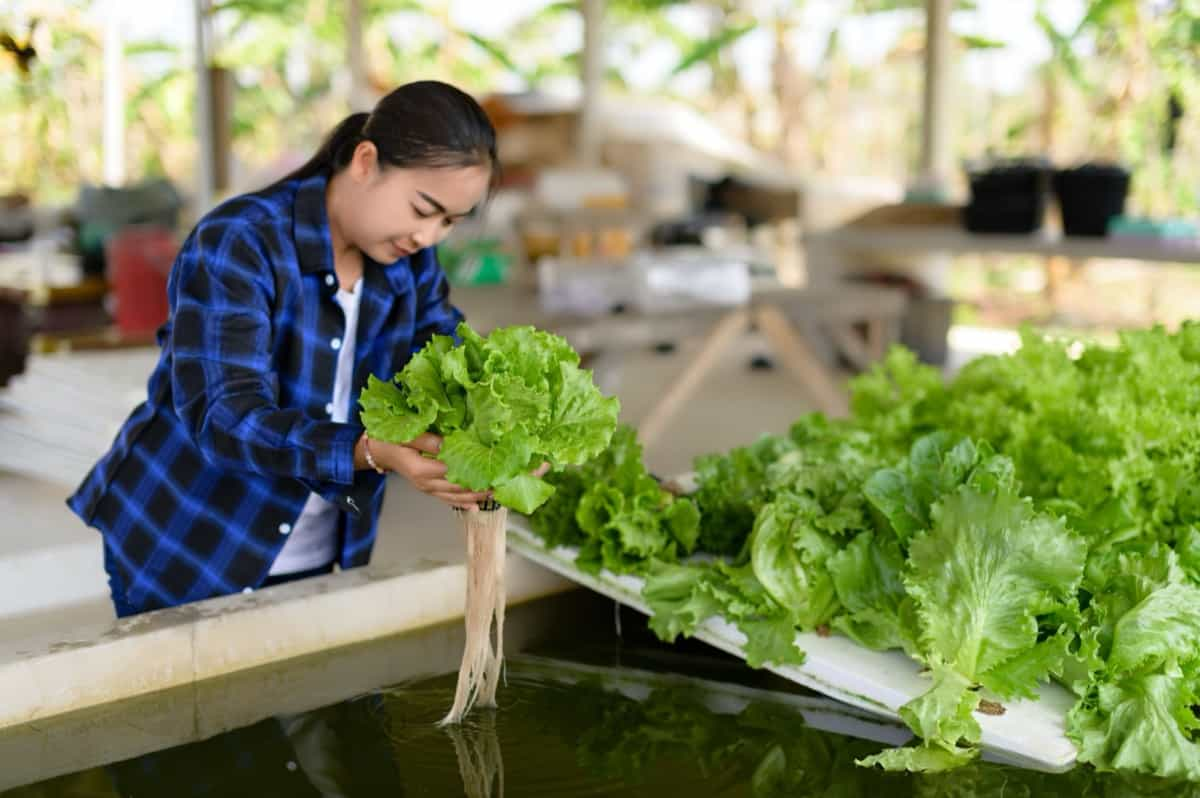

To build the system, connect the water pump to the solar panel, charge controller, battery, and inverter, drill holes in the grow bed, attach PVC pipes to create a drain and fill system, and place the air pump near the fish tank or pond. Fill the fish tank with water and plant seeds or seedlings in the grow bed. Test the system and adjust the flow rate and water level as needed.
Conclusion
15 DIY aquaponic plans offer eco-friendly gardening solutions for all levels of enthusiasts. With sustainable practices and the joy of growing both fish and plants, aquaponics brings science and nature together in your garden.
- Types of Pesticides Used in Agriculture: A Beginner’s Guide
- Economical Aquaculture: A Guide to Low-Budget Fish Farming
- 15 Common Planting Errors That Can Doom Your Fruit Trees
- How to Make Houseplants Bushy: Effective Tips and Ideas
- Innovative Strategies for Boosting Coconut Pollination and Yield
- Pollination Strategies for Maximum Pumpkin Yield
- The Complete Guide to Chicken Fattening: Strategies for Maximum Growth
- Natural Solutions for Tulip Problems: 100% Effective Remedies for Leaf and Bulb-Related Issues
- Revolutionizing Citrus Preservation: Towards a Healthier, Greener Future
- Natural Solutions for Peony Leaf and Flower Problems: 100% Effective Remedies
- Maximizing Profits with Avocado Contract Farming in India: A Comprehensive Guide
- Natural Solutions for Hydrangea Problems: 100% Effective Remedies for Leaf and Flowers
- The Ultimate Guide to Choosing the Perfect Foliage Friend: Bringing Life Indoors
- From Sunlight to Sustainability: 15 Ways to Use Solar Technology in Agriculture
- The Ultimate Guide to Dong Tao Chicken: Exploring from History to Raising
- The Eco-Friendly Makeover: How to Convert Your Unused Swimming Pool into a Fish Pond
- Mastering the Art of Delaware Chicken Farming: Essentials for Healthy Backyard Flocks
- 20 Best Homemade Fertilizers for Money Plant: DIY Recipes and Application Methods
- How to Craft a Comprehensive Free-Range Chicken Farming Business Plan
- Brighten Your Flock: Raising Easter Egger Chickens for Beauty and Bounty
- How to Optimize Your Poultry Egg Farm Business Plan with These Strategies
- Subsidy for Spirulina Cultivation: How Indian Government Schemes Encouraging Spirulina Farmers
- Ultimate Guide to Raising Dominique Chickens: Breeding, Feeding, Egg-Production, and Care
- Mastering the Art of Raising Jersey Giant Chickens: Care, Feeding, and More
- Ultimate Guide to Raising Legbar Chickens: Breeding, Farming Practices, Diet, Egg-Production
- How to Raise Welsummer Chickens: A Comprehensive Guide for Beginners
- How to Protect Indoor Plants in Winter: A Comprehensive Guide
- Ultimate Guide to Grow Bag Gardening: Tips, Tricks, and Planting Ideas for Urban Gardeners
- Guide to Lotus Cultivation: How to Propagate, Plant, Grow, Care, Cost, and Profit
- Agriculture Drone Subsidy Scheme: Government Kisan Subsidy, License, and How to Apply Online
- Ultimate Guide to Raising Araucana Chickens: Breed Profile, Farming Economics, Diet, and Care
- Bringing Hydroponics to Classroom: Importance, Benefits of Learning for School Students
- Ultimate Guide to Raising Polish Chickens: Breed Profile, Farming Economics, Diet, and Care
- Ultimate Guide to Raising Australorp Chickens: Profile, Farming Economics, Egg Production, Diet, and Care
- Silkie Chicken Farming: Raising Practices, Varieties, Egg Production, Diet, and Care
- Sussex Chicken Farming: Raising Practices, Varieties, Egg Production, Diet and Care
Awesome idea for kampong kita.