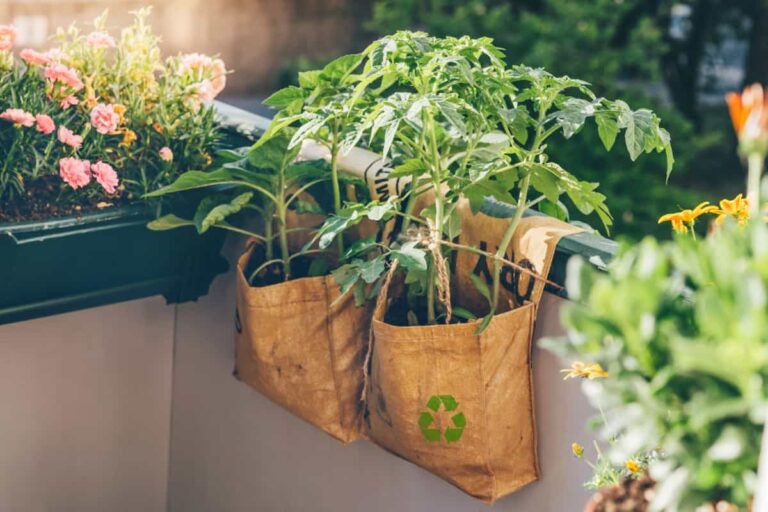
Discover the ultimate guide to grow bag gardening, perfect for urban gardeners seeking sustainable solutions. From fabric grow bags to DIY ideas, explore the versatility of container gardening. Learn about the best plants suited for growing bags and the ideal soil mix to foster healthy growth.

Uncover watering tips and pest management strategies tailored for grow bag gardens. Whether indoors or outdoors, on balconies or patios, embrace the benefits of this eco-friendly approach. Elevate your urban gardening experience with vertical gardening techniques and reusable grow bags.
All You Need to Know About Grow Bag Gardening
What are Grow Bags?
Grow bags are containers made from fabric materials that are specifically designed for gardening. Unlike traditional pots, grow bags allow plants’ roots to breathe, promoting healthier root development and overall plant growth. They are typically made from durable, non-woven fabric which provides excellent drainage, aeration for the plants. Grow bags come in various sizes, shapes, making them suitable for a different range of plants.
The Advantages of Using Grow Bags
- Grow bags allow plants’ roots to breathe, which is used for their overall health and growth. The fabric grow bags allows for better airflow and prevents root circling, which can occur in traditional pots.
- Grow bags are portable, easy to move, allowing you to position your plants in the best location for optimal sunlight and temperature conditions.
- Grow bags are lightweight and can be folded and stored when not in use, making them a convenient option for urban gardeners with limited space.
- Grow bags are cost-effective and reusable, making them a sustainable choice for gardening.
Choosing the Right Grow Bags
- Consider the size of the grow bags. Larger grow bags are suitable for plants with deeper root systems, while smaller ones are ideal for shallow-rooted plants.
- Consider the material of the grow bags. Fabric grow bags are the most common and recommended option as they provide excellent drainage and aeration for the plants.
- Look for grow bags with sturdy handles, as this will make them easier to move when filled with soil.
Getting Started with Grow Bags
- Choose a Suitable Location: Select a sunny spot for your grow bags, ensuring that your plants receive at least 6-8 hours of sunlight per day.
- Prepare the Grow Bags: Before filling the grow bags with soil, ensure they have drainage holes at the bottom to prevent waterlogging. You can use scissors or a gardening knife to create these holes.
- Fill the Grow Bags with Soil: Utilize a container gardening-specific, well-draining soil mix to ensure the plants receive the necessary nutrients and proper drainage.
- Plant Your Desired Plants: Select the appropriate plants for growing bag gardening (we will discuss suitable plants in detail later). Follow the recommended spacing guidelines for each plant to ensure proper growth and development.
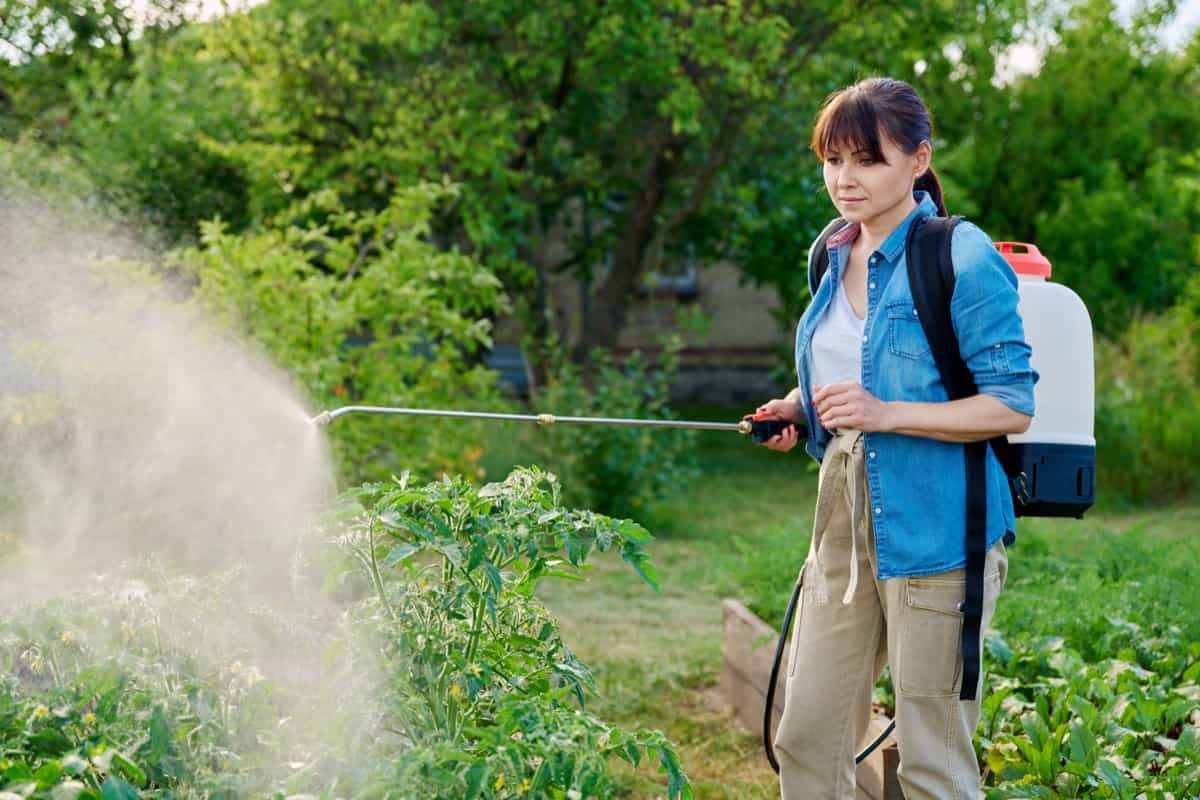
- Water and Maintain: Regularly water plants to maintain moist soil, monitor for pests or diseases, and take preventive measures for effective control.
Soil and Compost Mix for Grow Bags
- Use well-draining Soil: Grow bags require well-draining soil to prevent waterlogging and root rot. Well-draining soil allows water to flow in bag, ensuring that the roots can breathe.
- Use moisture-retaining Soil: While well-draining soil is important, it’s also essential to choose a soil mix that can retain moisture between waterings. This will help and prevent the plants from becoming thirsty and ensure they have a consistent water supply.
- Consider adding Compost: Adding compost to your soil mix can provide additional nutrients for your plants. Compost improves soil fertility and helps retain moisture, promoting healthy plant growth.
In case you missed it: Sustainable Living: The Growing Trend of Urban Apartment Gardening in India
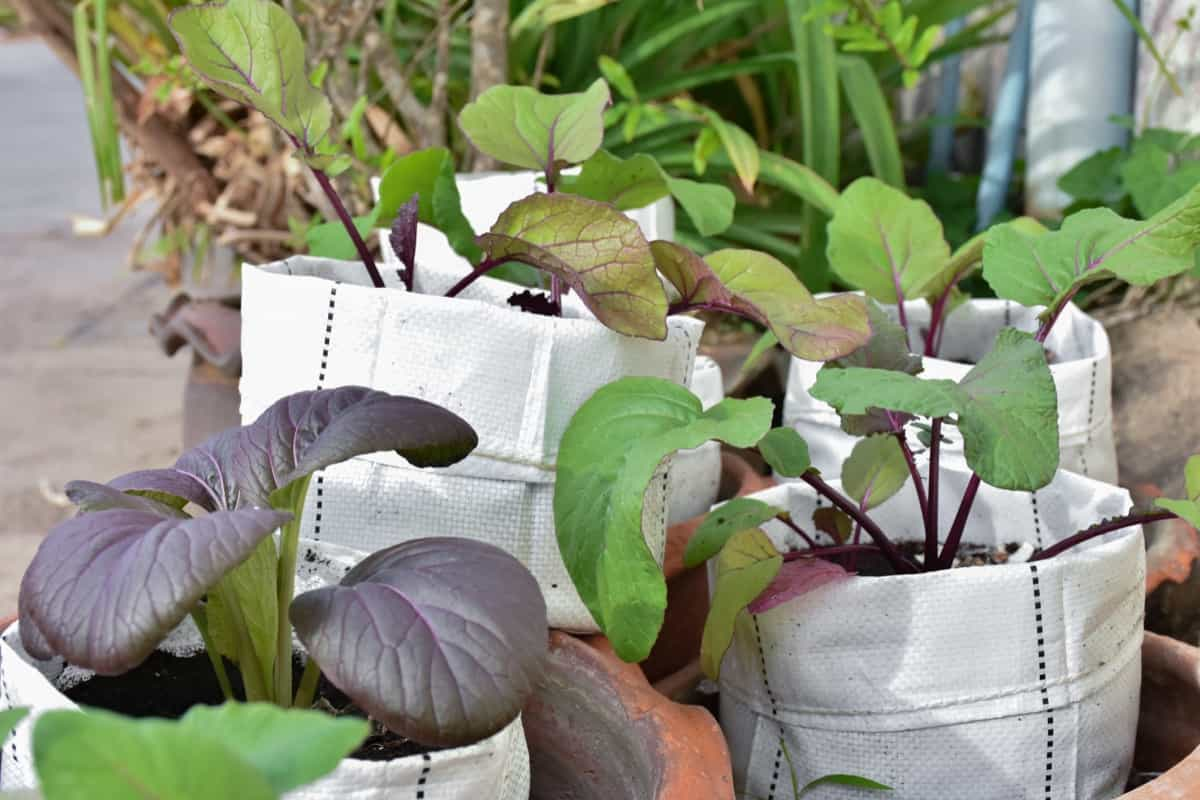

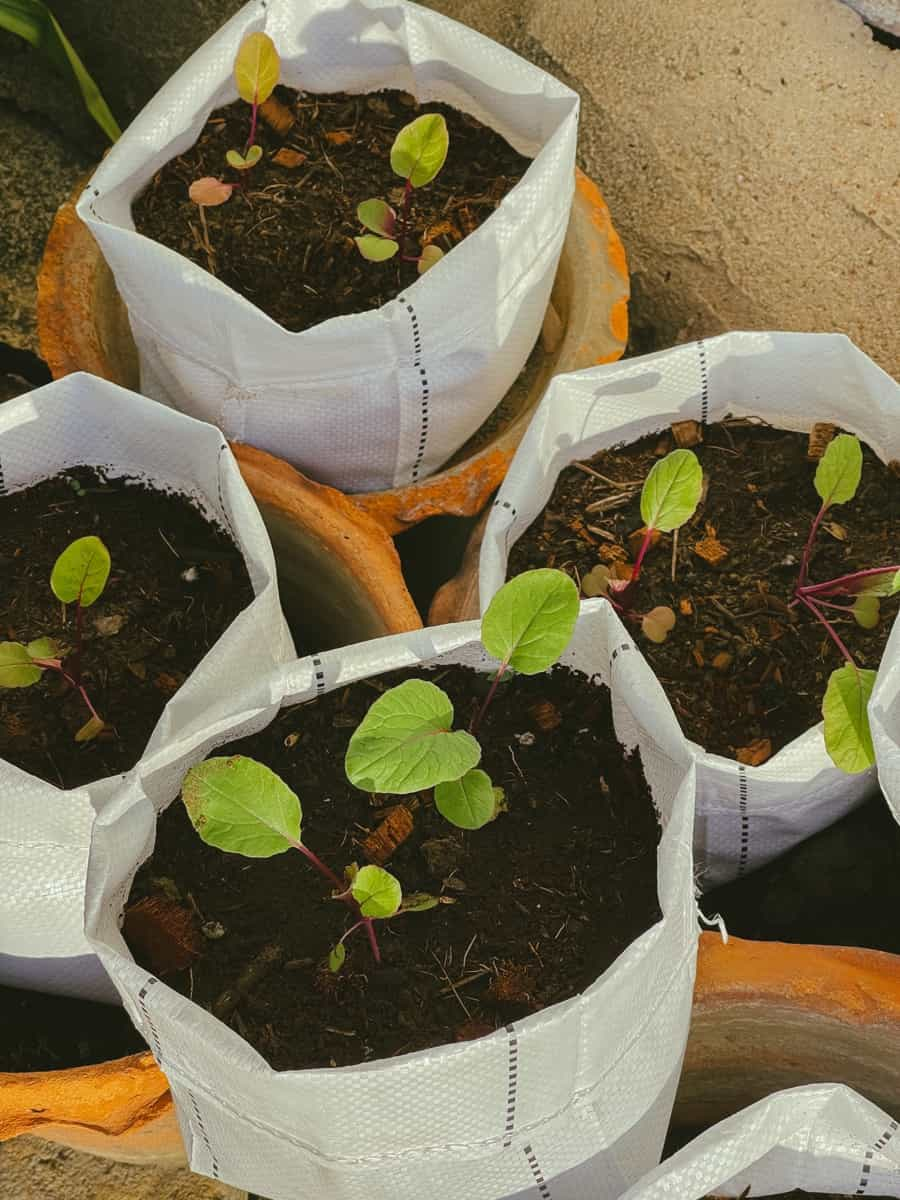
Plant Selection for Grow Bags
- Shallow-rooted Plants: Grow bags are best suited for shallow-rooted plants. Examples include tomatoes, peppers, lettuce, herbs, strawberries, and flowers.
- Compact and Bushy Plants: Choose plants that have a compact growth habit and don’t require extensive staking or support. This will help maximize space in your grow bags and prevent overcrowding.
- Consider the Mature Size: Take into account the mature size of the plants when selecting them for grow bags. Ensure that they have enough space to grow and develop properly without overcrowding.
Suitable Plants for Grow Bag Gardening
- Tomatoes: Compact varieties such as cherry tomatoes or determinate varieties are well-suited for grow bags. They provide a bountiful harvest and are relatively easy to grow.
- Peppers: Both sweet, hot pepper varieties can be grown successfully in grow bags. Choose compact varieties that don’t require extensive staking.
- Herbs: Herbs like basil, parsley, cilantro, and mint are excellent choices for growing bags. They are compact, easy to grow, and provide fresh flavors for your culinary creations.
- Lettuce and Salad Greens: Leafy greens like lettuce, spinach, and arugula can be grown in shallow grow bags. They are quick-growing and perfect for small-space gardening.
- Strawberries: Grow bags are an ideal option for growing strawberries. The elevated position of the bags helps prevent slugs and other pests from reaching the fruits.
Seasonal Planting Guide
- Spring: Plant cool-season crops like lettuce, spinach, radishes, and peas in early spring. These crops thrive in cooler temperatures, can be harvested in late spring or early summer.
- Summer: Plant warm-season crops like tomatoes, peppers, cucumbers, and beans in late spring or early summer. These crops require warmer temperatures and longer days to grow and produce a bountiful harvest.
- Fall: Plant cool-season crops again in late summer or early fall for a second harvest. Lettuce, kale, carrots, and beets are excellent choices for fall planting.
- Winter: In mild winter climates, you can continue growing cool-season crops throughout the winter. Protect your plants from frost and provide adequate insulation to ensure their survival.
Planting Techniques in Grow Bags
- Preparing Your Grow Bags: Before planting, make sure your grow bags have drainage holes at the bottom. This will prevent waterlogging and promote healthy root growth.
- Seed Sowing and Transplanting Tips: Follow the recommended seed sowing and transplanting guidelines for each plant. Start seeds indoors and transplant them into grow bags once they have developed strong roots.
- Spacing: Proper spacing is crucial to prevent overcrowding and ensure adequate airflow and sunlight for each plant. Follow the spacing recommendations provided for each plant variety.
Watering and Nutrition
- Watering Requirements for Grow Bags: Grow bags require more frequent watering compared to in-ground or raised-bed gardens. The fabric material of grow bags allows for faster evaporation, leading to quicker drying of the soil. Monitor the moisture levels regularly, water your plants when soil feels dry.
- Fertilizing Your Grow Bag Plants: Due to the limited volume of soil in grow bags, plants grown in them require more frequent fertilization. Use a balanced organic fertilizer and slow-release fertilizer to provide the necessary nutrients for your plants’ growth and development.
In case you missed it: The Growing Trend of Urban Terrace Gardening in India for Healthy Living and Sustainability

Pest and Disease Management
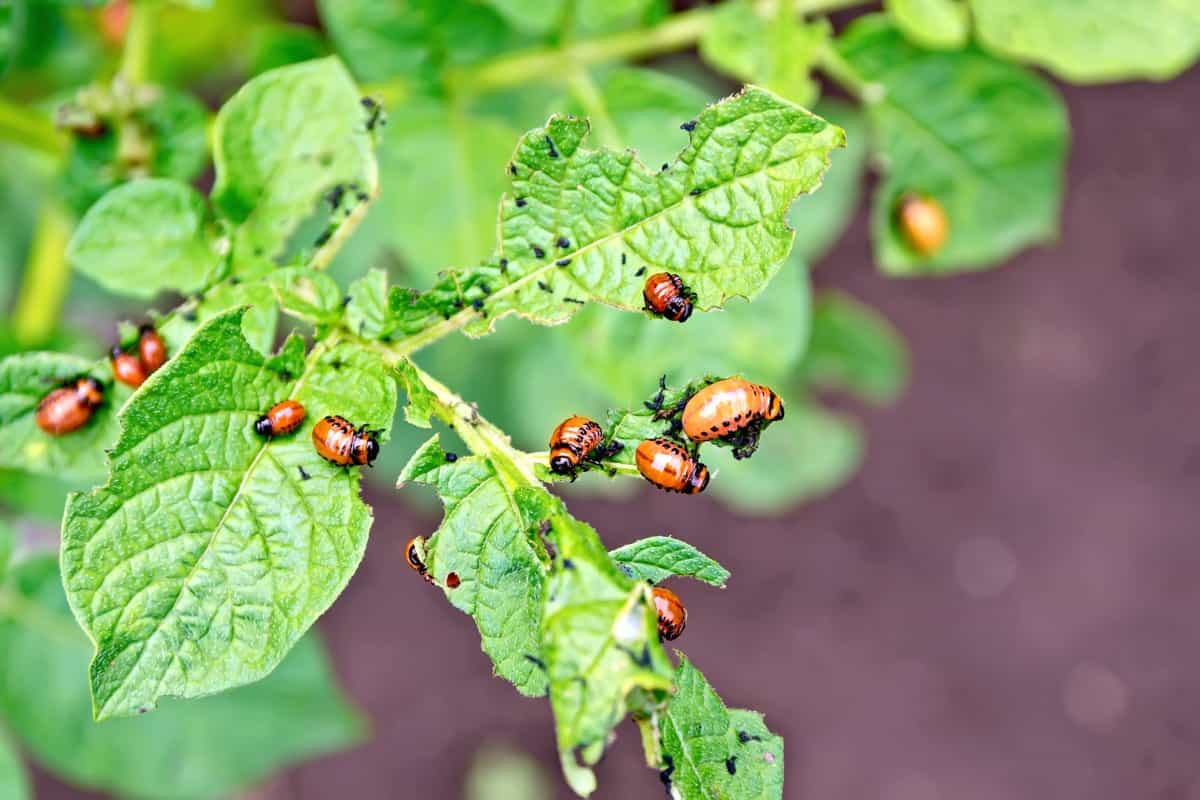
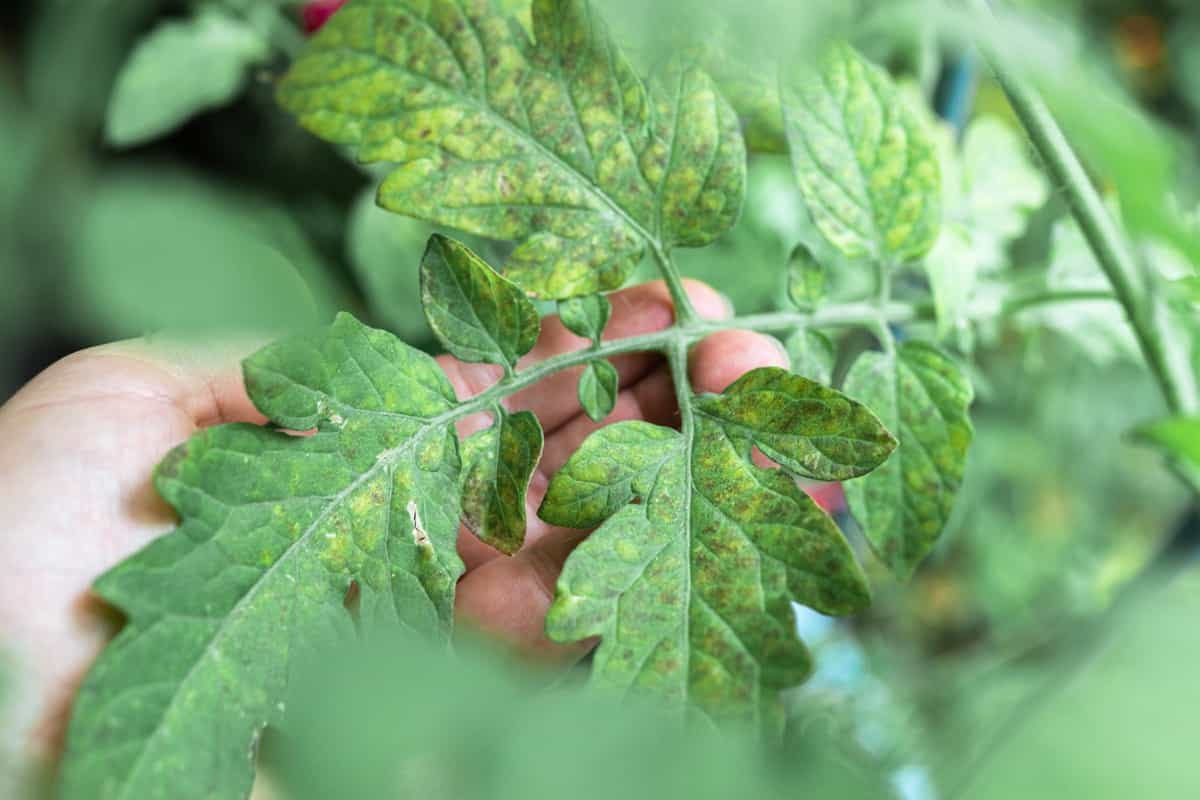
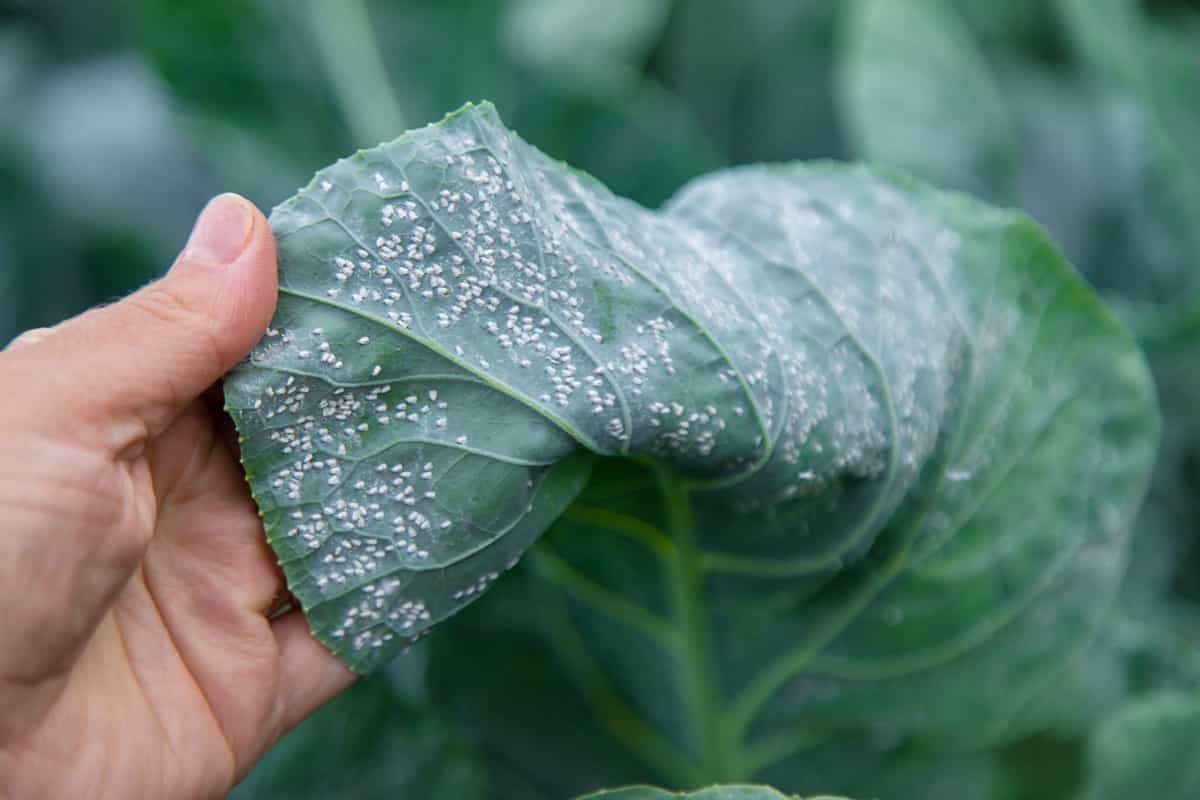
- Common Pests in Grow Bag Gardens: Some common pests that can affect grow bag gardens include aphids, thrips, slugs, snails, and caterpillars. Monitor your plants regularly and take appropriate measures such as handpicking, using organic pest control methods, or introducing beneficial insects to manage pest populations.
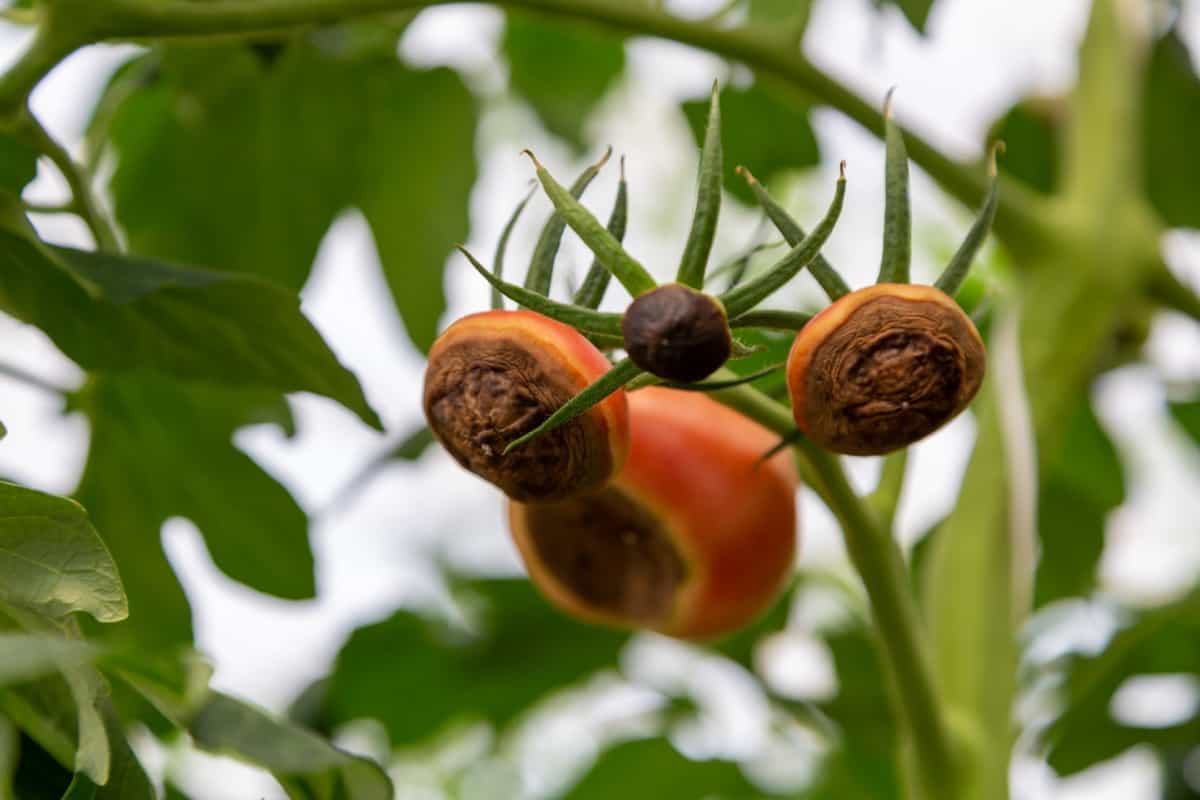
- Preventing Diseases in Grow Bags: To prevent diseases, ensure proper airflow and ventilation around your plants. Avoid overwatering, as excessive moisture can create a favorable environment for fungal diseases. If necessary, use organic fungicides or disease-resistant plant varieties.
Staking and Support
- Supporting Tall Plants in Grow Bags: Tall plants like tomatoes or pole beans may need support to keep them upright. Use stakes, trellises, or cages to provide support and prevent the plants from toppling over.
- DIY Staking Solutions: You can create your staking solutions using bamboo stakes, PVC pipes, or other sturdy materials. Secure the stakes firmly in the grow bags, tie the plants to stakes using soft plant ties or twine.
Maximizing Space with Grow Bags
- Vertical Gardening with Grow Bags: Utilize vertical space by growing vining plants like cucumbers or beans on trellises or vertical structures. Allows to grow multiple plants in a limited footprint.
- Companion Planting Strategies: Pair compatible plants together in the same grow bag to make the most efficient use of space. For example, plant lettuce and radishes together, as the radishes will mature before the lettuce needs the space.
- Intercropping: Plant fast-growing crops between slower-growing ones to maximize space. For example, plant lettuce or herbs between rows of tomatoes or peppers.
- Hanging Grow Bags: Hang grow bags from hooks or railing to create a vertical garden. Suitable for small balconies or patios where floor space is limited.
Seasonal Care for Grow Bag Gardens
- Preparing for Changing Seasons: As the weather transitions from one season to another, adjust watering and fertilization based on the changing needs of the plants. For example, decrease watering in cooler months to prevent over-saturation.
- Overwintering Grow Bag Plants: In colder climates, you can overwinter certain plants in grow bags by moving them to a protected area or providing insulation. Extend the growing season, continue harvesting fresh produce.
Harvesting from Your Grow Bag Garden
- Signs Your Plants are Ready for Harvest: Different plants have different signs that indicate they are ready for harvest. For example, tomatoes harvested should be firm and fully colored, while lettuce is ready when the leaves are mature and can be easily picked.
- Harvesting Techniques for Different Crops: Each crop requires specific harvesting techniques. Use pruning shears or scissors to harvest herbs, while you can gently twist or pull root vegetables like radishes and carrots from the grow bags.
Sustainability and Grow Bags
- Reusing and Recycling Grow Bags: After harvesting, empty the grow bags and reuse them for the next planting season. If the grow bags are damaged or worn out, recycle them appropriately.
- Making Your Grow Bag Garden More Sustainable: Use organic and natural fertilizers to reduce chemical inputs. Collect rainwater for watering your plants to conserve water. Compost kitchen scraps and plant waste to create nutrient-rich compost for your grow bags.
In case you missed it: Cultivating Plants in Recycled Plastic Bottles and Containers: New Art of Sustainable Gardening Practices

Common Challenges and Solutions
- Addressing Overwatering and Underwatering: Proper watering is crucial for growing bags. Avoid overwatering by monitoring soil moisture and adjusting watering frequency accordingly. If plants are underwatered, increase the watering frequency and ensure thorough hydration.
- Managing Soil Health in Grow Bags: Over time, the soil in grow bags can become depleted of nutrients. Mix the soil with compost and organic fertilizers regularly to ensure your plants have access to essential nutrients.
Advanced Tips for Grow Bag Gardening
- Experimenting with Hydroponics in Grow Bags: Explore the world of hydroponic gardening by adapting grow bags for hydroponic systems. Precise control over nutrient delivery, can result in faster growth and higher yields.
- Advanced Nutrient Management Techniques: Consider using specialized nutrient solutions or supplements to optimize plant growth and maximize yields. Conduct regular soil tests to monitor nutrient levels and make adjustments as needed.
Key Facts and Tips and Tricks for Urban Gardeners
Grow Bag Gardening: Experience the innovation of cultivating plants in fabric containers, revolutionizing traditional gardening methods.
Fabric Grow Bags: Invest in durable and breathable containers that provide optimal growing conditions for various garden plants, ensuring healthy root development and abundant yields.
Urban Gardening with Grow Bags: Ideal solution for urban dwellers facing space constraints, as fabric grow bags offer a compact and versatile option for cultivating greenery in city environments.
Best Plants for Grow Bags: Choose from a wide range of herbs, vegetables, and flowers that thrive in fabric grow bags, such as tomatoes, peppers, basil, lettuce, and marigolds, to name a few.
Reusable Grow Bags: Opt for environmentally friendly containers can be used for multiple growing seasons, reducing waste and promoting sustainable gardening practices.
Organic Gardening in Grow Bags: Commit to growing plants without synthetic chemicals in fabric containers, ensuring a healthier and more eco-friendly approach to gardening.
Watering Tips for Grow Bag Gardens: Master proper watering techniques to maintain soil moisture levels in fabric grow bags, ensuring optimal hydration for plant growth and development.
Soil Mix for Grow Bags: Create the perfect blend of soil, compost, and other amendments to provide essential nutrients and support for plant growth in fabric containers. Examples include a mixture of potting soil, perlite, and compost for optimal drainage and aeration.
Grow Bag Vegetable Gardening: Enjoy growing tomatoes, peppers, lettuce, carrots, and herbs like basil and parsley in fabric grow bags. These portable containers are perfect for balcony gardens or small outdoor spaces where traditional gardening isn’t feasible.
Indoor Gardening with Grow Bags: Enhance your indoor space with vibrant greenery by using compact fabric containers for growing houseplants like herbs (rosemary, thyme), leafy greens (spinach, kale), and small vegetables (cherry tomatoes, mini bell peppers).
In case you missed it: 17 Gardening Mistakes to Avoid This Summer: For Vegetables, Flowers, Herbs, and Fruits

Outdoor Grow Bag Setups: Transform your balcony or patio into a green oasis by arranging fabric grow bags filled with colorful flowers like petunias, marigolds, and geraniums. Grow herbs such as mint and lavender for added fragrance and culinary delight.
Vertical Gardening in Grow Bags: Utilize vertical space by hanging fabric grow bags filled with strawberries, trailing herbs like thyme and oregano, and compact vegetables such as cherry tomatoes and lettuce. This maximizes space while creating an eye-catching green wall.
Sustainable Grow Bag Options: Opt for eco-friendly grow bags made from recycled materials or biodegradable fabric. Examples include bags made from recycled plastic bottles or natural jute fiber, reducing environmental impact while promoting sustainable gardening practices.
Grow Bag Garden Design: Plan a stylish and functional garden layout by arranging fabric grow bags in creative patterns or tiers. Mix and match sizes and colors for visual interest, and incorporate trellises or stakes for vertical support when growing climbing plants like cucumbers or beans.
Grow Bags for Balconies and Patios: Utilize small outdoor areas efficiently with grow bags, allowing for gardening in limited spaces. Grow compact vegetables such as peppers and eggplants, along with dwarf varieties of fruits like strawberries and blueberries, to enjoy fresh produce even in urban settings.
In case you missed it: Gardening Tips for Beginners: At Home, in Pots/Containers, Indoors, On Terrace for Vegetables, Flowers, Fruits, and Herbs

Conclusion
Grow bag gardening offers urban gardeners a versatile and convenient way to grow their food. With the right selection of grow bags, suitable plants, proper care, and a sustainable approach, you can create a thriving and productive grow bag garden. So, get started with your own grow bag garden, enjoy the benefits of fresh and homegrown produce right at your fingertips.
- Goat Farming Technology: The Future of Goat Husbandry
- How to Build a Low-budget Goat Shed: Cheap Ideas and Tips
- Goat Farming Training Programs in India: A Beginner’s Guide
- Types of Pesticides Used in Agriculture: A Beginner’s Guide
- Economical Aquaculture: A Guide to Low-Budget Fish Farming
- 15 Common Planting Errors That Can Doom Your Fruit Trees
- How to Make Houseplants Bushy: Effective Tips and Ideas
- Innovative Strategies for Boosting Coconut Pollination and Yield
- Pollination Strategies for Maximum Pumpkin Yield
- The Complete Guide to Chicken Fattening: Strategies for Maximum Growth
- Natural Solutions for Tulip Problems: 100% Effective Remedies for Leaf and Bulb-Related Issues
- Revolutionizing Citrus Preservation: Towards a Healthier, Greener Future
- Natural Solutions for Peony Leaf and Flower Problems: 100% Effective Remedies
- Maximizing Profits with Avocado Contract Farming in India: A Comprehensive Guide
- Natural Solutions for Hydrangea Problems: 100% Effective Remedies for Leaf and Flowers
- The Ultimate Guide to Choosing the Perfect Foliage Friend: Bringing Life Indoors
- From Sunlight to Sustainability: 15 Ways to Use Solar Technology in Agriculture
- The Ultimate Guide to Dong Tao Chicken: Exploring from History to Raising
- The Eco-Friendly Makeover: How to Convert Your Unused Swimming Pool into a Fish Pond
- Mastering the Art of Delaware Chicken Farming: Essentials for Healthy Backyard Flocks
- 20 Best Homemade Fertilizers for Money Plant: DIY Recipes and Application Methods
- How to Craft a Comprehensive Free-Range Chicken Farming Business Plan
- Brighten Your Flock: Raising Easter Egger Chickens for Beauty and Bounty
- How to Optimize Your Poultry Egg Farm Business Plan with These Strategies
- Subsidy for Spirulina Cultivation: How Indian Government Schemes Encouraging Spirulina Farmers
- Ultimate Guide to Raising Dominique Chickens: Breeding, Feeding, Egg-Production, and Care
- Mastering the Art of Raising Jersey Giant Chickens: Care, Feeding, and More
- Ultimate Guide to Raising Legbar Chickens: Breeding, Farming Practices, Diet, Egg-Production
- How to Raise Welsummer Chickens: A Comprehensive Guide for Beginners
- How to Protect Indoor Plants in Winter: A Comprehensive Guide
- Ultimate Guide to Grow Bag Gardening: Tips, Tricks, and Planting Ideas for Urban Gardeners
- Guide to Lotus Cultivation: How to Propagate, Plant, Grow, Care, Cost, and Profit
- Agriculture Drone Subsidy Scheme: Government Kisan Subsidy, License, and How to Apply Online
- Ultimate Guide to Raising Araucana Chickens: Breed Profile, Farming Economics, Diet, and Care
- Bringing Hydroponics to Classroom: Importance, Benefits of Learning for School Students
- Ultimate Guide to Raising Polish Chickens: Breed Profile, Farming Economics, Diet, and Care