Embark on a journey through the intricacies of Elderberry Farming with our comprehensive guide. Delve into Propagating Elderberries, explore diverse Elderberry Varieties, and master Planting techniques. Learn about Elderberry Yield Per Acre, delve into Profit prospects, and discover Organic Cultivation methods. Uncover market trends, harvest insights, and sustainable practices.

Guide to Elderberry Farming
Introduction to Elderberry Farming
Elderberry farming is a rewarding and sustainable way to grow a versatile and healthy fruit. Elderberries are native to North America and can thrive in various climates and soil types. They have many benefits for both humans and the environment, such as boosting immunity, attracting pollinators, and preventing erosion.
Overview of Elderberry Benefits and Uses
The plant elderberry offers a wide range of applications and health advantages. Elderberry berries and blooms are rich in antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals that enhance and strengthen the immune system, shield the heart, and stave off cancer. In addition, elderberry helps lower fever, ease coughing, improve digestion, and treat cold and flu symptoms. Dried berries or elderberry juice might also have laxative and diuretic properties. Elderberries, however, should be prepared before consumption since they can be toxic when raw or underripe.
Market Demand for Elderberries
Elderberries, small purple berries with health benefits, are rich in antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals. They boost the immune system and are used in various products. The market demand for elderberries is increasing, with a CAGR of 6.50%, expected to reach $600 million by 2030.
Understanding Elderberry Varieties
Elderberries are versatile and productive plants that can offer many benefits to the home gardener. They produce beautiful flowers and tasty berries that can be used for food and medicine. However, not all elderberry varieties are the same, and some factors need to be considered before choosing the best one for your garden.
Popular Varieties for Cultivation
Adams, Johns, Nova, and York are native American varieties of grapes, each with unique characteristics. Adams produces medium-sized, juicy purple fruits, while Johns produces large, dark, tart berries suitable for jam and jelly. Nova and York are compact varieties, producing semi-sweet, fresh berries. The University of Missouri’s Bob Gordon variety, with its high sugar content, is ideal for winemaking.
Selecting the Right Variety for Your Climate
Adams is a cold-hardy variety of elderberry that thrives in moist, fertile soils and full sun. It can tolerate acidic and alkaline soils, partial shade, and drought. For colder regions, choose a variety that can withstand low temperatures and frost. For wet areas, choose a variety that can handle excess moisture. Plant compatible varieties near each other for cross-pollination.
In case you missed it: How to Manage Pests and Diseases in Berry Orchards: A Comprehensive Guide

Propagating Elderberries
Elderberries can be easily propagated through various methods, including cuttings, seeds, and division. Each method offers its advantages and considerations.
Methods of Propagation: Cuttings, Seeds, and Division
- Cuttings: Take stem cuttings from healthy elderberry plants in the dormant season, usually late fall to early spring, and root them in a suitable growing medium.
- Seeds: Collecting ripe elderberry seeds, stratifying them for a few months, then sowing them in a prepared seedbed or container.
- Division: Dividing mature elderberry plants by carefully separating the root mass into sections with shoots attached.
Preparing Propagation Material
- Cuttings: Select healthy, disease-free stems with a diameter of about pencil-thickness. Cut them into sections around 6 to 8 inches long, ensuring each cutting has at least one node.
- Seeds: Extract seeds from ripe elderberries, remove any pulp, and then stratify them in a moist medium, such as peat moss or vermiculite, for 2 to 3 months.
- Division: Before dividing, water the elderberry plant thoroughly to make the soil easier to work with. Then, carefully lift the plant and use a sharp tool to separate the root mass into sections, ensuring each section has adequate roots and shoots.
Soil Preparation and Requirements
Elderberries thrive in well-drained soil with a pH level between 5.5 and 6.5. Soil should be rich in organic matter and free from compaction. Before planting, keep the soil loose and friable, allowing roots to establish easily. Incorporating compost or aged manure can improve soil structure and fertility, providing essential nutrients for healthy growth.
Ideal Soil Conditions for Elderberries
Elderberries prefer loamy soil that is rich in organic matter and drains well. Acidic to neutral pH levels ranging from 5.5 to 6.5 is optimal for nutrient uptake. Adequate soil moisture retention is important, but saturated conditions should be inhibited to prevent root rot. Good air circulation around the roots also promotes healthy growth and reduces disease risks.
Soil Amendments and Preparation Techniques
Before planting elderberries, amend the soil with organic matter, including compost or well-aged manure to improve fertility and structure. Incorporating perlite or vermiculite can enhance drainage in heavy soils. Use a shovel or tiller to loosen compacted soil, ensuring roots can penetrate easily. Remove weeds or debris from the planting area to reduce competition.
Planting Elderberries
Choose wholesome elderberry plants from a reliable source. Create a massive hole that is twice as large and deep as the plant’s root ball. Carefully remove the plant from the plant container and place it in the center of the hole. Make sure the plant is at the same level as it was in the container by backfilling it with dirt.
Best Time to Plant
When the weather is chilly and wet, in early spring or late autumn, elderberries grow best. In doing so, the plants are able to form roots prior to the arrival of summer heat or winter cold. Planting should be avoided when there is a severe heat wave or drought since these conditions can stress plants and lower their chances of surviving.
Planting Techniques for Optimal Growth
Elderberries need at least 6 feet between plants in order to have enough airflow and area to flourish. Mulch should be applied around the base of the plants to control soil temperature, prevent weed growth, and preserve moisture. Watering on a regular basis is crucial, particularly in dry or droughty conditions. Every year, prune to encourage new growth and get rid of any dead or damaged wood.
Irrigation and Water Management
Elderberry farms require consistent and efficient irrigation systems to thrive. Drip irrigation is a popular choice, delivering water directly to the roots while minimizing water wastage. Additionally, mulching around elderberry plants helps retain moisture, reducing the need for excessive watering. Proper water management is important to ensure optimal growth and yield of elderberries while conserving water resources.
In case you missed it: How to Control Pests and Diseases in Strawberry Crop: Causes, Symptoms, Chemical, and Biological Management

Irrigation Systems for Elderberry Farms
Elderberry farms benefit from various irrigation systems tailored to their specific needs. Drip irrigation, using perforated hoses or tubing, emits water directly to the base of the plants, minimizing water loss through evaporation and runoff. Overhead sprinklers can also be effective, especially for larger farms, although they may require more water and can increase the risk of foliar diseases.
Watering Schedule and Requirements
Following a consistent watering schedule is essential for elderberry plants’ health and productivity. During the growing season, elderberries typically require around 1 to 1.5 inches of water per week, either from rainfall or supplemental irrigation. However, it’s crucial to monitor moisture levels and adjust watering frequency based on weather and plant needs to prevent over or under-watering.
Fertilization and Soil Management
Maintaining healthy soil fertility is vital for elderberry production, requiring a balanced approach to fertilization and soil management. Regular soil testing helps determine nutrient deficiencies, allowing growers to tailor fertilization strategies accordingly. Incorporating compost or aged manure improves soil structure and nutrient retention, promoting healthy root development and overall plant vigor.
Nutrient Requirements for Elderberries
Elderberries have specific nutrient requirements to support their growth and development. They benefit from a well-balanced fertilizer containing nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, and micronutrients. Nitrogen is essential for foliage growth, while phosphorus aids in root development and flower production. Potassium supports both disease resistance and general plant health. Micronutrients such as manganese, iron, and zinc are also essential for the nutrition of elderberries.
Organic and Inorganic Fertilization Strategies
Depending on their tastes and output objectives, growers can select between organic and inorganic fertilization techniques. Organic fertilizers offer gradual nutrient release and enhance soil health since they are made from natural sources like compost, manure, or plant leftovers. Inorganic fertilizers, on the other hand, offer precise nutrient formulations and immediate availability, allowing for more targeted nutrient management.
Pest and Disease Management
In elderberry cultivation, it’s crucial to manage pests and diseases to ensure healthy plant growth and optimal yield. Common pests include aphids, spider mites, and Japanese beetles, while diseases such as powdery mildew and bacterial leaf spot can also affect elderberry plants. Implementing Integrated Pest Management (IPM) practices is essential to minimize pesticide use and maintain a balanced ecosystem.
Common Pests and Diseases in Elderberry Cultivation
Elderberries are vulnerable to various pests and diseases, impacting their growth and yield. Among the most common pests are aphids, which suck sap from plants, causing leaf curling and stunted growth. Additionally, elderberry borers can bore into the stems, leading to weakened branches and decreased productivity. Diseases, including powdery mildew and bacterial leaf spot, can also affect elderberries, causing leaf discoloration and fruit deterioration.
Integrated Pest Management (IPM) Practices
Integrated Pest Management (IPM) combines various strategies to control pests while minimizing environmental impact and maintaining economic viability. These practices include monitoring pest populations, employing biological control methods like introducing beneficial insects, using cultural techniques such as crop rotation, and utilizing chemical control only when necessary as a last resort. IPM aims to achieve sustainable pest control while preserving natural ecosystems.
In case you missed it: Top 15 Steps to Boost Blueberry Yield: How to Increase Production, Size, and Quality

Pruning and Plant Management
Pruning plays a vital role in managing elderberry plants for optimal growth and fruit production. Proper pruning techniques are involved.
- Removing dead or diseased branches.
- Thinning out crowded areas to improve air circulation.
- Shaping the plant to encourage robust growth and easy harvesting.
Additionally, managing plant density by spacing plants appropriately ensures each plant receives adequate sunlight and nutrients for maximum yield.
Pruning Techniques for Elderberry Plants
When pruning elderberry plants, start by removing any dead or damaged branches and cutting them back to healthy wood. Next, thin out overcrowded areas by selectively removing some branches to improve air circulation and light penetration. Shape the plant by cutting back lateral branches to encourage upward growth and facilitate harvesting. Regular pruning promotes vigorous growth and minimizes the risk of disease.
Managing Plant Density for Optimal Yield
Pruning plays a vital role in managing elderberry plants for optimal growth and fruit production. Proper pruning techniques involve removing dead or diseased branches, thinning out crowded areas to improve air circulation, and shaping the plant to encourage robust growth and easy harvesting. Additionally, managing plant density by spacing plants appropriately ensures each plant receives adequate sunlight and nutrients for maximum yield.
Pollination and Berry Production
Pollination is vital for elderberry farming as it ensures the transfer of pollen, leading to fruit formation. Elderberries, rich in antioxidants and vitamins, rely on pollinators like bees for efficient fertilization. This process significantly impacts berry yield and quality, making pollination management crucial for successful elderberry cultivation.
Importance of Pollination in Elderberry Farming
Pollination plays a crucial role in elderberry farming by facilitating fruit set and development. Effective pollination leads to increased berry production, contributing to higher yields and improved fruit quality. Adequate pollination ensures genetic diversity within elderberry crops, enhancing their resilience to environmental stresses and diseases, thereby promoting sustainable farming practices.
Enhancing Pollination through Beekeeping or Natural Pollinators
Farmers can enhance pollination in elderberry cultivation by maintaining healthy populations of bees or encouraging the presence of natural pollinators. Beekeeping practices such as hive placement and habitat conservation create favorable conditions for pollinators, leading to improved fruit set and yield. Additionally, incorporating diverse plantings and minimizing pesticide use support the abundance of natural pollinators.
Harvesting Elderberries
Harvesting elderberries at the optimal stage of ripeness is crucial for maximizing yield and quality. Proper timing ensures that berries are flavorful and nutrient-rich, ideal for consumption or processing. Recognizing the signs of ripeness and employing appropriate harvesting techniques are essential steps in obtaining a bountiful elderberry harvest.
Signs of Ripeness and Harvesting Time
Elderberries are ready for harvest when they turn deep purple or black and feel plump and firm to the touch. Fully ripe berries should easily detach from the stem with minimal effort. Harvesting typically occurs in late summer to early fall, coinciding with peak ripeness and flavor development in elderberries.
Harvesting Techniques to Maximize Yield and Quality
To maximize yield and quality, adopt careful harvesting techniques that minimize damage to the berries and plants. Utilize sharp pruning shears or scissors to gently clip clusters of ripe elderberries from the stem, avoiding excessive bruising or crushing. Harvesting during cooler temperatures and dry weather conditions further preserves berry freshness and flavor.
Post-Harvest Handling and Processing
Proper post-harvest handling and processing are essential for preserving the freshness and nutritional value of elderberries. Swiftly clean and dry harvested berries to prevent spoilage and maintain quality. Implementing appropriate storage practices and exploring various processing options enable value addition and extend the shelf life of elderberry products.
In case you missed it: Bolting Management in Plants: Prevention for Premature Flowers and Seeding in Crops and Vegetables
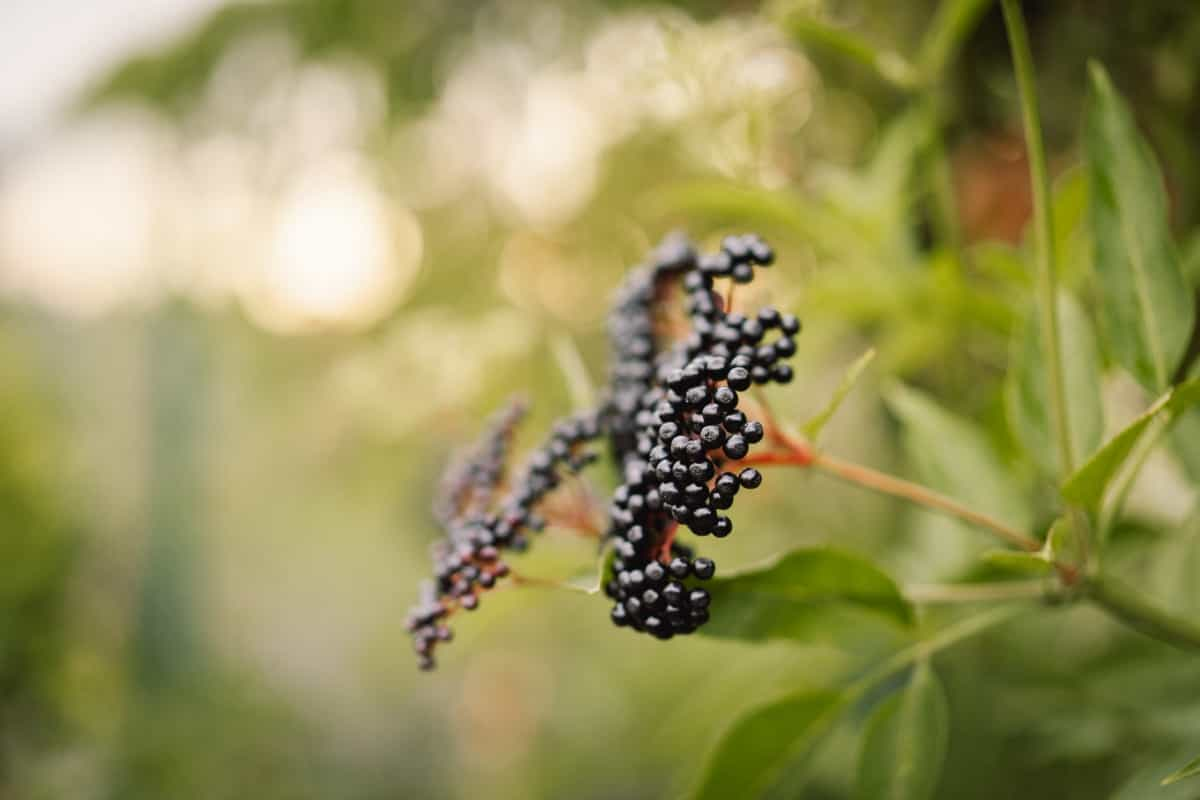
Cleaning, Drying, and Storage of Elderberries
After harvesting, carefully clean elderberries by removing any debris or damaged berries. Spread them in a single layer on trays or screens to air dry thoroughly, ensuring moisture content is reduced to prevent mold growth. Store dried elderberries in airtight containers in a cool, dark place to maintain their flavor, color, and nutritional integrity.
Processing Options for Value Addition
Elderberries offer versatile processing options for value addition, including making jams, syrups, juices, and wines. Explore recipes and techniques for transforming fresh or dried elderberries into a range of delicious and nutritious products. Consider experimenting with different flavor combinations and preservation methods to create unique elderberry-based offerings for culinary enjoyment and health benefits.
Yield Expectations and Factors Influencing Yield
Elderberry yield expectations vary based on factors such as climate, soil quality, and cultivation practices. A well-managed elderberry farm can typically yield between 3,000 to 6,000 pounds per acre, although this can fluctuate significantly depending on various environmental and agricultural variables.
Average Yield per Acre
The average yield per acre of elderberry can range from 3,000 to 6,000 pounds under optimal conditions. However, this figure is subject to change due to factors like weather patterns, soil fertility, pest control measures, and the age and health of the elderberry plants on the farm.
Factors Affecting Elderberry Yield
Several factors influence elderberry yield, including climate, soil composition, moisture levels, sunlight exposure, plant spacing, pruning techniques, fertilization practices, and pest and disease management. Each of these elements plays an important role in determining the overall productivity and profitability of elderberry cultivation endeavors.
Costs of Starting and Running an Elderberry Farm
Starting an elderberry farm requires careful financial planning, including land purchase, equipment, planting materials, labor, and marketing efforts. Running costs include recurring costs for fertilizers, pesticides, labor, utilities, insurance, and marketing efforts, as well as ongoing expenses for maintenance and operations.
Initial Setup Costs
According to Finmodelslab, the initial setup costs for an elderberry farm include land acquisition, site preparation, planting materials, irrigation system, tools and equipment, and legal fees. The total amount may vary depending on the size and location of the farm, but a rough estimate is $50,000 for a 10-acre farm.
Recurring Expenses and Cost Management
The recurring expenses for an elderberry farm include labor, water, fertilizer, pest and disease control, pruning, harvesting, processing, packaging, marketing, and transportation. These costs can be reduced by adopting efficient management practices, such as mulching, pruning, intercropping, organic farming, and direct marketing. The average annual operating cost for a 10-acre farm is estimated at $25,000.
Profitability and Revenue Streams
An elderberry farm’s profitability hinges on the yield, quality, and price of berries. Average yield: 12,000 lbs/acre. Quality varies by size, color, flavor, and nutrients. Average price: $3/lb. Revenue streams include fresh/frozen berries, juice, jelly, wine, syrup, and extracts.
Calculating Potential Profits from Elderberry Farming
Elderberry farming profits are calculated by subtracting total expenses from total revenue. Revenue is yield multiplied by berry price. For instance, a 10-acre farm yielding 120,000 lbs at $3/lb earns $360,000. Expenses include operating costs ($25,000/yr) and setup ($50,000 amortized over ten years), totaling $30,000. Thus, the potential profit for a 10-acre farm is $330,000 ($360,000 – $30,000).
Diversifying Revenue through Value-Added Products
Diversifying elderberry farm revenue through value-added products like juice, jelly, wine, syrup, extract, tea, and cosmetics can increase profitability. These processed items cater to niche markets and can be marketed as organic, local, or medicinal products to fetch premium prices.
Marketing Strategies for Elderberry Products
- Identifying target demographics.
- Emphasizing health benefits.
- Utilizing social media platforms.
- Collaborating with influencers.
- Offering samples.
- Creating visually appealing packaging to attract consumers.
In case you missed it: How to Increase Flowering in Fruit Trees: Step-by-Step Guide for Beginners
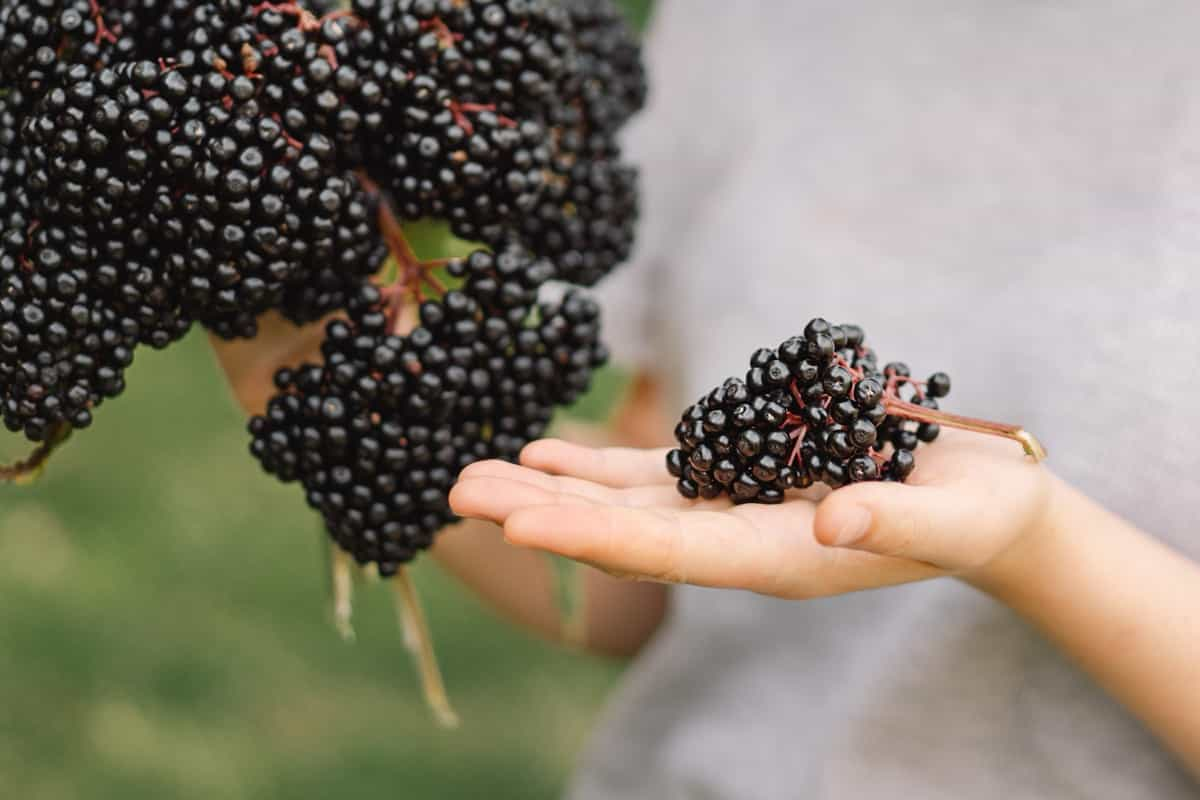

Identifying Your Market: Fresh, Dried, or Processed Products
Whether you’re selling fresh, dried, or processed elderberry products, understanding your target market is crucial. Fresh elderberries appeal to health-conscious consumers looking for natural remedies, while dried or processed products attract those seeking convenience or specific culinary uses. Conduct market research to pinpoint your audience’s preferences.
Digital and Traditional Marketing Techniques
To reach potential customers effectively, combine digital and traditional marketing techniques. Utilize social media platforms to showcase your elderberry products, engage with customers, and run targeted ads. Additionally, consider traditional methods like attending trade shows, partnering with local retailers, or advertising in relevant publications to expand your reach.
Sustainability and Organic Certification
Consumers increasingly prioritize sustainability and organic certification when purchasing food products. Obtaining organic certification for your elderberry products can enhance credibility and attract environmentally conscious customers. To stand out from the competition, highlight your brand’s dedication to ethical supply chains and sustainable agricultural methods.
Practices for Sustainable Elderberry Farming
Implementing sustainable farming practices is essential for long-term viability and environmental stewardship. Practices including crop rotation, natural pest control methods, and water conservation can minimize ecological impact and promote soil health. Additionally, investing in renewable energy sources and reducing waste can further enhance sustainability efforts on elderberry farms.
Process and Benefits of Organic Certification
Strict requirements and inspections are necessary to get organic certification in order to verify adherence to organic farming practices. Gaining access to upscale markets, gaining the confidence of customers, and raising the price of organic elderberry goods are some advantages. A company’s reputation and customer loyalty are enhanced by certification, which shows a dedication to health-conscious and environmentally responsible business operations.
Conclusion
Mastering Elderberry Farming involves understanding every aspect, from Propagation to Marketing. Selecting the right Elderberry Varieties, coupled with proper Planting and Soil Preparation, maximizes Yield Per Acre. Efficient Pest Management and Irrigation Systems ensure Sustainable Cultivation. Post-harvest processing and Marketing strategies enhance Profit, meeting rising Market Demand. Organic Certification adds value, expanding Revenue Streams.
- Types of Pesticides Used in Agriculture: A Beginner’s Guide
- Economical Aquaculture: A Guide to Low-Budget Fish Farming
- 15 Common Planting Errors That Can Doom Your Fruit Trees
- How to Make Houseplants Bushy: Effective Tips and Ideas
- Innovative Strategies for Boosting Coconut Pollination and Yield
- Pollination Strategies for Maximum Pumpkin Yield
- The Complete Guide to Chicken Fattening: Strategies for Maximum Growth
- Natural Solutions for Tulip Problems: 100% Effective Remedies for Leaf and Bulb-Related Issues
- Revolutionizing Citrus Preservation: Towards a Healthier, Greener Future
- Natural Solutions for Peony Leaf and Flower Problems: 100% Effective Remedies
- Maximizing Profits with Avocado Contract Farming in India: A Comprehensive Guide
- Natural Solutions for Hydrangea Problems: 100% Effective Remedies for Leaf and Flowers
- The Ultimate Guide to Choosing the Perfect Foliage Friend: Bringing Life Indoors
- From Sunlight to Sustainability: 15 Ways to Use Solar Technology in Agriculture
- The Ultimate Guide to Dong Tao Chicken: Exploring from History to Raising
- The Eco-Friendly Makeover: How to Convert Your Unused Swimming Pool into a Fish Pond
- Mastering the Art of Delaware Chicken Farming: Essentials for Healthy Backyard Flocks
- 20 Best Homemade Fertilizers for Money Plant: DIY Recipes and Application Methods
- How to Craft a Comprehensive Free-Range Chicken Farming Business Plan
- Brighten Your Flock: Raising Easter Egger Chickens for Beauty and Bounty
- How to Optimize Your Poultry Egg Farm Business Plan with These Strategies
- Subsidy for Spirulina Cultivation: How Indian Government Schemes Encouraging Spirulina Farmers
- Ultimate Guide to Raising Dominique Chickens: Breeding, Feeding, Egg-Production, and Care
- Mastering the Art of Raising Jersey Giant Chickens: Care, Feeding, and More
- Ultimate Guide to Raising Legbar Chickens: Breeding, Farming Practices, Diet, Egg-Production
- How to Raise Welsummer Chickens: A Comprehensive Guide for Beginners
- How to Protect Indoor Plants in Winter: A Comprehensive Guide
- Ultimate Guide to Grow Bag Gardening: Tips, Tricks, and Planting Ideas for Urban Gardeners
- Guide to Lotus Cultivation: How to Propagate, Plant, Grow, Care, Cost, and Profit
- Agriculture Drone Subsidy Scheme: Government Kisan Subsidy, License, and How to Apply Online
- Ultimate Guide to Raising Araucana Chickens: Breed Profile, Farming Economics, Diet, and Care
- Bringing Hydroponics to Classroom: Importance, Benefits of Learning for School Students
- Ultimate Guide to Raising Polish Chickens: Breed Profile, Farming Economics, Diet, and Care
- Ultimate Guide to Raising Australorp Chickens: Profile, Farming Economics, Egg Production, Diet, and Care
- Silkie Chicken Farming: Raising Practices, Varieties, Egg Production, Diet, and Care
- Sussex Chicken Farming: Raising Practices, Varieties, Egg Production, Diet and Care