Pomelo Cultivation Guide:

Introduction of Pomelo Fruit: – The Pomelo fruit belongs to citrus race and are closely related to Grapefruit. Pomelo belongs to the family of “Rutaceae” and genus of citrus. Pomelo scientific name is Citrus Maxima or Citrus Grandis and these fruits are native to South and Southeast Asia. Pomelo is a largest fruit in the citrus world. The thick and yellow skinned fruit is popularly known in the western world as Pomelo (Pummelo,pommelo), shaddock, batavia lemon or pamplemousse. In India, this fruit is known as “Chakotras”. However, this name also technically indicates the Grapefruit though both are different species under citrus genus. The fruit is consumed as fresh and is also used in cooking to make desserts and jellies. This fruit can weigh up to 10 kg. The Pomelo fruit has the taste of Grapefruit without the much bitterness and acidity and the texture is fleshy and has more membrane than many other types of citrus fruits.
Health benefits of Pomelo Fruit:- Some of the health benefits with Pomelo fruit are as follows.
- The Pomelo fruit prevents UTI (Urinary Tract Infection)
- The Pomelo fruit helps in preventing common cold & flu
- The Pomelo fruit helps in healing of wounds
- The Pomelo fruit helps in prevention of anaemia
- The Pomelo fruit promotes healthy teeth & gums
- The Pomelo fruit regulates blood pressure levels
- The Pomelo fruit helps in prevention of leg cramps
- The Pomelo fruit helps in curing constipation
- The Pomelo fruit helps in preventing osteoporosis
- The Pomelo fruit aids in weight loss
- The Pomelo fruit has antioxidant and anti-fungal properties

Pomelo Varieties and Major Production States in India:-
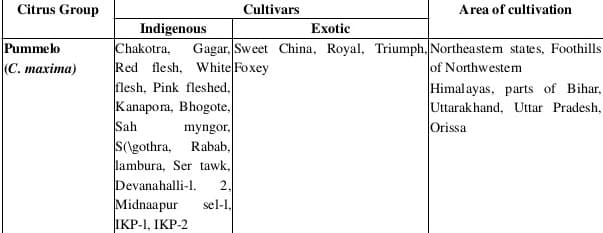
Pomelo Local Names in India:- Common names: Pomelo, Jabong, Pummelo, Pommelo Shaddock and Chinese grapefruit.
Sadaphal (Hindi), Chakotha Hannu (Kannada), Pampara Panasa/Dabba Kayaa (Telugu), Chakotra (Bengali), Pamparamasan/Kambili Naranga (Malayalam), Gadarangai (Tamil), Toranji (Konkani), Papanas (Marathi).
Soil and Climate Requirement for Pomelo Cultivation:- The Pomelo fruit can be grown on wide variety of soils from coarse sand to heavy clay. However, it grows best in the deep, medium-textured, fertile soils in lowland tropics and elevation not exceeding 400 masl (meters above sea level). The best soil pH is 5.5 to 6.5 and the optimum temperature of 25°C to 32°C is required along with annual rainfall of 150 cm to 180 cm for its best growth and yield.
Propagation in Pomelo Cultivation:- Pomelo can be propagated sexually by seed or asexually by air layering , grafting, budding & stem cuttings. In South east Asia, the most common propagation method is air layering.
Land Preparation, Spacing and Planting in Pomelo Cultivation: – Land should be prepared to the fine tilth stage by giving 2 or 3 ploughings and harrowing with desi plough. This also cleans and weeds from previous crops and level the land. If the soil acidic in nature, applying lime to the soil will be helpful. Pits should be dug about 0.5 deep and wide. In Pomelo farming, the plant spacing of 8 to 10 meter x 6 to 8 meter should be maintained which will approximately accommodate about 125 to 210 plants per 1 hectare land. Supplement the pits with compost at the bottom or mixed at about 1/3 proportion with the topsoil which will be used to refill the pits after planting. In case of raw manure is used, it is recommended to delay the planting for 2 weeks.
The best planting season in Pomelo cultivation is during the onset of the monsoon. Planting can be done any time where irrigation facility is available. Drip irrigation would be opted for best effective management of water.
Irrigation in Pomelo Cultivation:- Irrigation depends on the soil moisture holding capacity and growth stage of the plants. The first irrigation should be carried out immediately after planting to ensure contact of the plant roots with soil. Frequent irrigations should be given before flowering. To force early flowering, watering should be delayed during the dry season until the plant shows signs of wilting. Then the wilting trees should be irrigated. However, for new growth of the shoots and development of the fruits, frequent irrigation is needed. Usually, an adult tree requires 100 to 250 liters of water daily during hot summer period. Drip irrigation can be adopted for effective management of water.
Intercropping in Pomelo Cultivation:- Farmers should always utilize the inter spaces in the main crop to generate some extra income. In Pomelo farming, inter crops like banana and areca palm or any vegetable crops can be cultivated during young plantation. Later any shade loving inter crops would be beneficial.
Weed Control in Pomelo Cultivation:- Pomelo crop requires regular weeding to eliminate competition for soil moisture and nutrients. Mulching at the plant base can check the weed growth along with using recommended weedicides.
Pruning in Pomelo Cultivation:- After 5 to 6 months of planting, pruning should be carried out to induce branching. This should be done by top pruning about 30 to 45 cm from the ground level. 3 to 4 branches which are evenly distributed in separate horizontal directions should be retained and allowed to grow.
Fertilizers in Pomelo Cultivation:- Along with organic manure, it requires chemical fertilization for better production. Foliar fertilizer can also be applied every new flushes. NPK combination of 13-13-21 is used to improve fruit taste. It should be applied in 2 doses, first dose before flowering and other one after 5 to 6 months. Fertilizers should be increased on yearly basis based on the tree age. The fertilizers should be applied in the pits about 1 to 2 meters from the trunk. Spraying of foliar fertilizer also recommended for every 20 days starting at 40 days after planting until 140 days after fruit set.
Pests and Diseases in Pomelo Cultivation:- Generally, most of the pests and diseases which attack the citrus crop will be found in Pomelo cultivation as well. These are common leafminers , leaf-eating caterpillars, red mites, fruit-boring caterpillar, fruit flies, scales, rats and nematodes. For control measures of these, contact local horticulture department.
Harvesting in Pomelo Cultivation:- Usually, Pomelo fruits will be ready for harvesting in 5 months to 6 months from fruit set (Note: not after planting).The dull skin of the fruit brightens once started ripening as the oil glands become more prominent and shiny.
Yield in Pomelo Cultivation:- Generally, yield of any crop depends on the cultivar (variety), weather conditions and cultivation practices. An average yield of 75 to 100 fruits per tree/year or 20 tons/ha per year can be obtained.
For Sheep or Goat Farming Info in India : Read Here.
If too many flowers and fruits come out on one pomelo tree, is there a need for fruit thinning and how?