Introduction to Vegetable Farming Tips, Techniques, Ideas in India
Vegetable farming means growing vegetable crops mainly for use as human food. Successful vegetable farming requires the grower to make daily decisions regarding soil requirements, pest management, irrigation, and cultural practices. Vegetable plants have the advantage of giving a relatively quick return. Most vegetable plants only take 6 weeks to 6 months between planting and harvesting.
Commercial vegetable farming has an important part of the agriculture business. It has supported the livelihood of farmers through household subsistence farming to commercial-scale business. Vegetables are an excellent source of vitamins like niacin, riboflavin, Thiamin, and vitamins A and C. They also supply minerals like calcium and iron besides proteins and carbohydrates. Most of the vegetables, being short duration crops, fit well in the intensive cropping system and are capable of giving high yields and also providing better health standards to the people.
A Step by Step Guide to Vegetable Farming Tips, Techniques, Ideas, Business Plan
Vegetable farming accomplished only when maximum stand establishment is achieved. Stand reduction results in reduced yields and variable product quality. Several factors contribute to standing establishment in the production of vegetable crops. Environmental factors like soil, temperature, etc., as well as pathogens that attack seeds and seedlings, contribute to reduced stands. Understanding both the influence of the seed planted and the soil conditions in which the seed is sown is necessary for crop establishment. Staggered emergence results in seedlings of several sizes. Plant cultural practices like herbicide and insecticide applications after emergence may be less effective in fields of non-uniform growth. Plants of different sizes within one population also cause problems in timing side-dress applications.
Vegetable cultivation is a type of crop production intended mainly for human consumption. According to the consuming part of the crop, vegetable plants are divided into the following groups;
- Leafy vegetables (Lettuce, Cabbage, Spinach)
- Fruit vegetables (Pepper, Cucumber, Tomato)
- Root vegetables (Carrot, Radish, Sweet Potato)
- Bulb vegetables (Garlic, Onion, Fennel)
- Flower vegetables (Artichoke, Cauliflower, Broccoli)
Types of Vegetable Production
In developed countries the three main types of vegetable farming are based on vegetable production for the fresh market, for processing means canning, freezing, dehydration, and pickling, and to obtain seeds for planting.
Production for the fresh market – This is mainly divided into home gardening, market gardening, truck farming, and vegetable forcing.
Home gardening provides vegetables for family use. Desirable home vegetable garden crops Bean, Cabbage, Carrot, Leek, Lettuce, Onion, Parsley, Pea, Pepper, Radish, Spinach, and Tomato. Market gardening produces different vegetable plants for a local market. Truck farming produces specific vegetable plants in large quantities for distant markets. Vegetable plants are produced out of their normal season of outdoor production under forcing structures for plant growth in vegetable forcing.
Production for processing – Processed vegetables includes canned, dehydrated, frozen, and pickled products. The cost of production per unit area of land and per ton is less for processing crops than for the same crops grown for the market because raw material appearance is not a major factor in processing. This difference allows lower land value, less hand labor, and lower handling cost.
Conditions for vegetables for canning and freezing include small size, high quality, and uniformity. Acceptable processed vegetables have a taste, odor, and appearance compared with the fresh product and has good storage stability.
Vegetables raised for seed production – This farming requires special skills and methods. Different methods are applied during the flowering and seed development stages and also in harvesting and threshing the seeds.
Points and Tips to Consider in Starting Vegetable Farming
A vegetable farming business demands proper planning, investment, and marketing. However, here we have discussed some of the basic points to start vegetable farming.
- First of all, to start any business planning is necessary.
- Then, figure out how much area you have
- According to the agro-climatic condition select the vegetable for farming.
- You must consider the local market. Because vegetables are hugely perishable items.
- Also, cultivate the scope of export.
- Select the right plant species.
- Also, you must arrange the proper irrigation for your farm.
- Plan for harvesting storage.
- Calculate the entire working capital cost.
- Finally, you must arrange the required finance.
Vegetable Farming Tips and Ideas for Beginners
- Types of Pesticides Used in Agriculture: A Beginner’s Guide
- Economical Aquaculture: A Guide to Low-Budget Fish Farming
- 15 Common Planting Errors That Can Doom Your Fruit Trees
- How to Make Houseplants Bushy: Effective Tips and Ideas
- Innovative Strategies for Boosting Coconut Pollination and Yield
- Pollination Strategies for Maximum Pumpkin Yield

Profitable vegetable farming requires attention to some operations such as pest, disease, and weed control, and efficient marketing. Effective management involves some methods resulting in a steady flow of the desired amount of produce over the whole of the natural growing season.
Climate – Climate involves the temperature, daylight, moisture, and wind conditions of a specific region. Climatic factors strongly affect all stages and processes of crop growth.
Site Selection – Most vegetable plants do best in full sun. Find a location that gets at least 6 hours of it each day if possible. Also, with the continued trend toward specialization, relatively large areas are required for commercial production, and transportation facilities are necessary.
Plant High-Yield Vegetables – Make the most of your time and space by growing vegetable plants that produce a high crop yield. Some of the high yield crops are Tomatoes, Onions, and Lettuce. They need the least amount of space and time, but give the most valuable yields in return. Melons, Winter Squash, and Pumpkins are fun to grow, but take much more space and produce little.
Temperature – Temperature requirements are based on the minimum, optimum, and maximum temperature levels during day and night throughout plant growth. Requirements change according to the type and variety of the specific crop. Based on their optimum temperature changes, vegetable crops may be classified as cool-season or warm-season types.
Daylight – Sunlight is the most important thing for any cultivation. Vegetables require at least 6 hours of sun each day and if you can get 8 hours, that’s better.
Soil preparation – Soil preparation in vegetable farming involves the usual operations required for other crops. Air is essential to the growth of crops and to certain beneficial soil organisms making nutrients available to the plants. In vegetable production, soils are managed intensively. Most vegetable plants require fine preparation and land leveling for optimum use of water. Soil preparation can happen at any time of the year, due to the variety of vegetable production. Conventional and reduced tillage are common practices, with growing awareness among farmers of the benefits that reduced tillage delivers. Direct seeding experiences are still uncommon for most vegetable plants. The number of soil operations is variable, but usually includes one or several passes for land preparation after the previous crop (that can include early applications of fertilizers); weed treatments (mechanical or using agrochemicals), and seeding/planting.
Water wisely – The most efficient and productive method to irrigate is by using soaker hoses and drip lines. Automatic timers are a great method to take the effort and worry out of this all-important step.
Nutrients – Vegetable plants are high nutrient demanding crops. Repeated applications of fertilizers in vegetable growing fields without knowing their fertility status creates a severe imbalance of nutrients. All essential plant nutrients are present in the soil system available or complex forms.
Care of vegetable crops during growth – Some practices required for plant growth include cultivation, irrigation, fertilizers application, control of weeds, diseases, and insects; and the application of growth regulators if necessary.
Vegetable harvesting – Harvesting vegetables at the right time can have a big impact on crop yield and quality. Depending on the type of vegetable, several devices are employed to harvest produce. Normally used vegetable harvesting tools are secateurs or knives, and handheld or pole-mounted picking shears.
In case if you are interested in this: Organic Papaya Farming.
Factors that Determine Successful Vegetable Production
There are a few factors that influence the profitability of vegetable production;
- Seed quality; the sowing of quality, clean, graded to size, viable, and healthy seed can make all the difference between success or failure in the vegetable farming business
- Optimal time of sowing or planting; depends on climate conditions of the specific location, as well as requirements of each vegetable crop
- Method of planting; the secret to successful vegetable farming lies in the managing of crop requirements, by combining the production of transplants in the greenhouses with planting in the field
- Considering effective management is the main step in creating profitable vegetable farming. In essence, farming of these colorful crops can be a profitable vegetable business.
Classification of Vegetables Based on Usage
- Pot herbs or greens – Spinach, Kale, New Zealand Spinach, Mustard, Chard, Collards, and Dandelion
- Salad crops – Celery, Chicory, Lettuce, Watercress, and Endive
- Cole crops – Cabbage, Brussels Sprouts, Cauliflower, Kohlrabi, Sprouting Broccoli, and Chinese Cabbage
- Root crops – Beet, Turnip, Carrot, Rutabaga, Parsnip, Radish, and Celeriac
- Bulb crops – Onion, Garlic, Leek, Shallot, and Welsh Onion
- Pulses or legumes – Peas, and Beans including dry-seeded or agronomic forms
- Cucurbits – Cucumber, Pumpkin, Muskmelon, Squash, and Watermelon
- Solanaceous fruits – Tomato, Pepper, Eggplant, and Husk Tomato
Vegetable Farming Techniques
1. Vegetable Seed Production
Seed production in vegetables is the limiting factor for vegetable cultivation in India. The vegetable plants require specific temperature and other climatic conditions for flowering and fruit set. To reduce such microclimatic conditions a protected environment is necessary. For example, Summer Squash requires a mild climate for flowering, fruit setting and fruit development, and seed formation. Seed production of highly remunerative crops such as Capsicum, Tomato, and Cucumber is performed in a protected environment.
Vegetable farming in the low-and medium-cost greenhouse is a technical reality in India. Such a production system has not only extended the vegetables growing season but also encouraged the conservation of different rare vegetable plants. The vegetable seed production under a protected environment is important to increase vegetable production in India.
2. Organic Vegetable Production
Vegetable growers may wish to consider organic production. The initial investment is high in this production, due mainly to certification costs. Though, returns can be higher than for conventionally produced products. Organic vegetable farming is a challenging process for new farmers. As they do not have enough experience and knowledge about organic cultivation.
Organic vegetable production is management-intensive and requires careful attention to the maintenance of a biological equilibrium favorable for crop production. Organic certification gives growers increased market access, but requires learning new production systems and documenting production practices through careful record keeping. Though, when implemented well, organic methods can improve soil fertility and tilth through increased soil microorganisms and improved organic matter recycling. Organic farming is replete with products that do not necessarily work. Growers should test new methods on a small scale before large scale adoption.
Soil Requirements Tips and Management in Organic Vegetable Farming
The components that are used in organic vegetable farming are Manures, Bio-fertilizers, Vermicomposting, Green Sand, Rock phosphate, Nitrogen, Potassium, Phosphorus, Bone Meal, and green manure crops, etc. The soil health in terms of organic carbon, bulk density, water-holding capacity, and microbial biomass carbon and dehydrogenase activity is improved under the organic system as compared to the inorganic system.
Organic Vegetable List;
Organic or natural non-chemical agriculture methods can grow any vegetable plants. A list of most profitable and popular organic vegetables is given below;
- Spinach, Swiss chard, Greens, Herbs, Kale and Kohlrabi, Leeks, and Lettuce.
- Broccoli, Cabbage, and Cauliflower.
- Peas, and Beans.
- Corn, Tomatoes, Cherry Tomatoes, Zucchini, Okra, and Eggplant.
- Squash and Pumpkins, Cucumbers, Watermelons, Melons
- Carrots, Turnips, Rutabagas, Radishes, Parsnips, and Beets.
- Potatoes, and Onions.
Tips to Control Pests in Organic Vegetable Farming
Some organic methods to control pests in vegetable plants are;
- Build healthy, compost heavy soil.
- Ensure Better quality compost.
- Choose disease immune vegetable seeds or plants.
- Monitor vegetable growth stages.
- If there is any affected plant, pull out them.
- Wet foliage favors insect and fungal. So keep it dry.
- Water sufficiently in the dry season.
- Protect plants from the direct sun using the shed, particularly in the early stage.
- Mulching should be practiced when needed.
- Apply for organic certification.
Flow Chart of Vegetable Farming Techniques
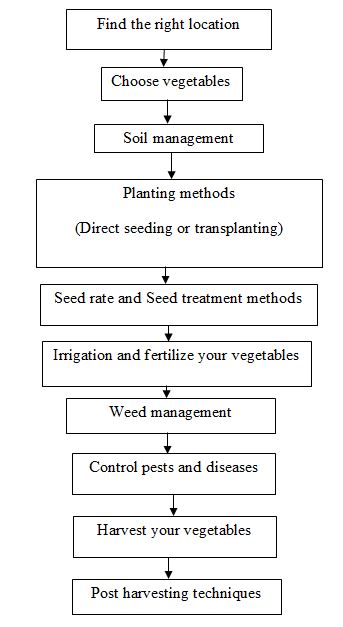
Improved Vegetable Production Practices and Farming Tips
Examples of improved production techniques for some vegetable crops like Tomato, Cabbage, Rape, Onion, Okra, and Cucurbits were discussed below;
Site selection – Site selection is very important in vegetable production to take crop adaptation to soils, climate, and market considerations.
Seed selection – Seed selection mainly involves sources of seed, characteristics of good seed, using high-quality seed, adaptability, seasonal adaptation, resistance to diseases, disadvantages of using recycled seeds.
Nursery Management – Nursery requirements are site selection, rotation, good sanitation, and irrigation, fertilizers, pest, and disease management.
Land preparation – Land preparation means the importance of good tilth, different tillage systems raised beds and flatbeds. Suitability of tillage systems based on season, soil types, irrigation methods respectively.
Fertilizers – Sources of nutrients – organic (compost, green and cattle manure) and inorganic fertilizers. Using green manure crops, compost, and livestock manure to improve soil fertility. Maintaining soil fertility and plant nutrient supply to sustain the desired level of vegetable production. This is to be achieved through the following;
- By using balanced mineral fertilizers combined with organic and biological sources of plant nutrients.
- Improving and maintaining the stock of plant nutrients in the soils.
- Improving efficiency use of nutrients by avoiding environmental losses.
Seed rate – Crop growth is based on using recommended seed rates.
Spacing – The importance of using optimum spacing for high yields were emphasized.
Crop rotation – The implications of good crop rotations to minimize pests and disease build-up and to enhance soil fertility.
Irrigation/Water management – Moisture requirements for different crops and critical growth stages to avoid moisture stress.
Pest and disease management in crops – This is the biggest problem in vegetable farming. Proper pest and disease identification are important to plant growth. An integrated approach to pest and disease management mainly involving cultural, biological, cultivar resistance and use of pesticides.
Weed control – The importance of weeding was emphasized to avoid competition for space, nutrients, water. Certain weeds like Nicandra are alternate hosts for red spider mites.
Post-harvest handling – It mainly involves proper harvesting methods, time of harvest, care in the handling of produce, use of field storage sheds, proper packaging materials, treatment of produce, and grading of produce.
In case if you are interested in this: How To Start Vegetable Selling Business In India.